1、Istio安装配置
Istio安装配置
本节实战
| 实战名称 |
|---|
🚩 实战:istioctl 方式安装istio-2023.11.3(测试成功) |
| 🚩 实战:手动注入 Envoy Sidecar-2023.11.3(测试成功) |
| 🚩 实战:自动注入 Envoy Sidecar-2023.11.8(测试成功) |
| 🚩 实战:BookInfo 示例应用-2023.11.5(测试成功) |
| 🚩 实战:自定义一个端口访问应用-2023.11.6(测试成功) |
目录
[toc]
前言
前面在服务网格基础章节我们和大家已经了解了 Istio 的基本概念以及架构,本章节我们将来快速了解 Istio 的基本使用方法,对 Istio 有一个最基本的认识。

1、安装
安装 Istio 之前,需要准备一个 Kubernetes 集群,我们可以使用任何支持的平台,例如 Minikube、Kind、Kubeadm 等,但是需要注意的是目前的 Istio 最新版本为 v1.19.3 版本,不同的版本支持的 Kubernetes 版本不同,可以参考下表进行对照:
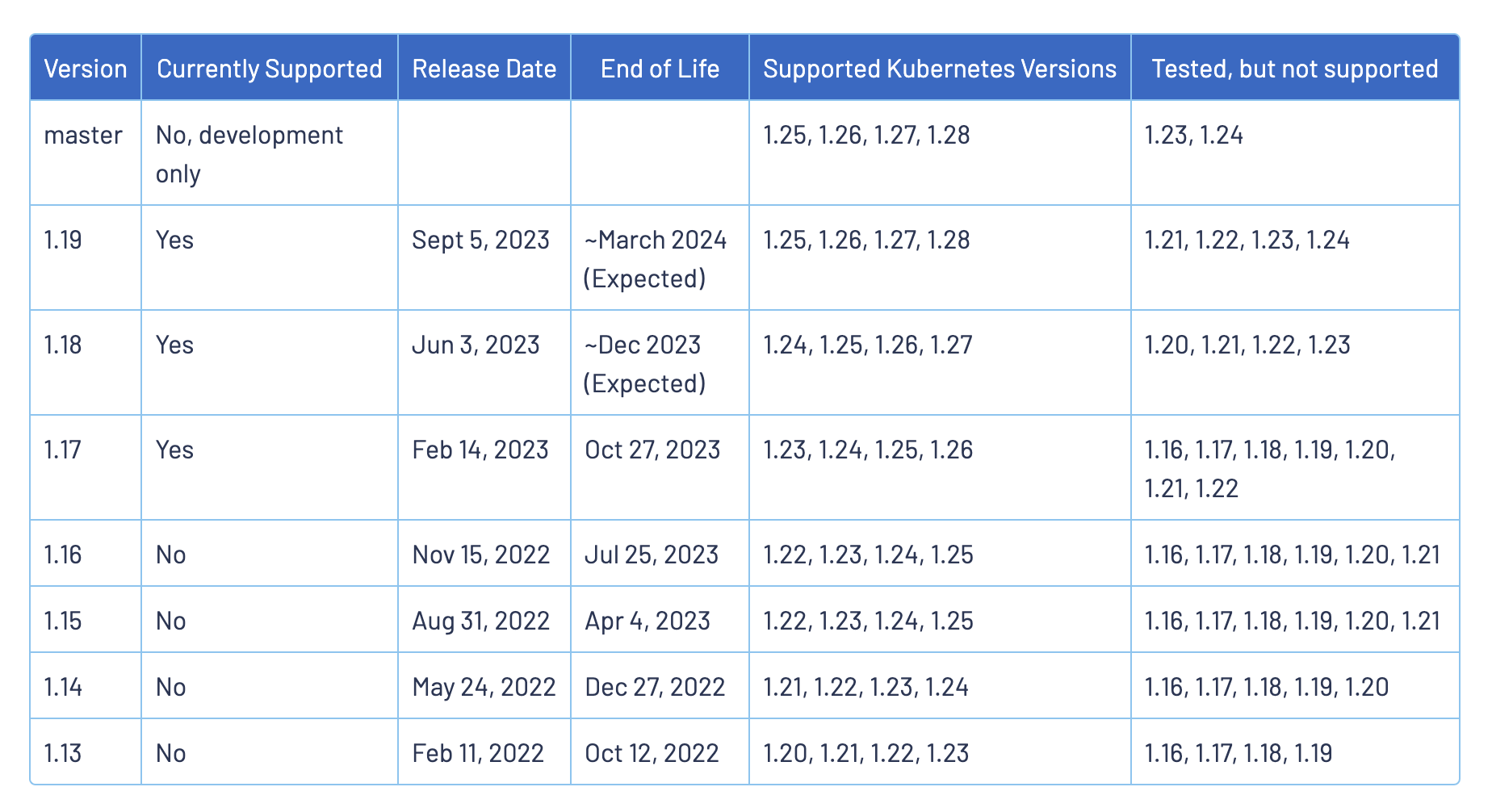
我们这里选择最新的版本为 v1.19.3,Kubernetes 版本为 v1.27.6:
$ kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
master1 Ready control-plane 43d v1.27.6
node1 Ready <none> 43d v1.27.6
node2 Ready <none> 43d v1.27.6安装方式
在 Kubernetes 集群上安装 Istio 的方法有很多方式,可以根据自己的需求选择不同的安装方式,我们可以先对比下每种方式的优缺点。
1.使用 istioctl install
具有高安全性、简单的安装和管理方法,这也是社区推荐的安装方法。
优点:
完整的配置和运行状态的验证。
使用提供了扩展的配置、自定义选项的
IstioOperatorAPI。不需要集群内的高权限 Pod,通过执行
istioctl命令修改。
缺点:
需要维护多个 Istio 版本的二进制文件。
istioctl命令可能根据你的运行环境设置诸如JWT_POLICY之类的值,从而在不同的 Kubernetes 环境中产生不同的安装结果。
整体来说,这里的缺点对我们可能影响不大。
2.使用 istioctl manifest generate 安装
生成 Kubernetes 的配置清单,并通过 kubectl apply --prune 命令应用到集群中。该方法适用于需要严格审查或者增加配置清单的情况。
优点:
Chart 是由与
istioctl install和 Operator 里使用的相同的IstioOperatorAPI 生成的。使用提供了扩展的配置、自定义选项的
IstioOperatorAPI。
缺点:
一些在
istioctl install和 Operator 中会进行的检查将不会执行。与
istioctl install相比,UX 不够简洁。错误反馈没有
istioctl install的详细、全面。
3.使用 Helm 安装
使用 Helm 的 Chart 可以通过 Helm 的工作流轻松的完成,并在升级的过程中自动清理资源。
优点:
使用熟悉、常用的行业标准工具。
Helm 原生的版本、升级管理。
缺点:
相比于
istioctl install和 Operator 相比,检查较少。一些管理任务需要更多步骤,具有更高的复杂性。
4.使用 Istio Operator 安装
不建议在新安装时使用 Operator,虽然 Operator 将继续得到支持,但新的功能特性不会被优先考虑。
Istio Operator 提供了一种安装路径,无需使用 istioctl 二进制文件。这可以用于简化升级工作流程,不必担心在集群中运行特权控制器的问题。此方法适用于不需要严格审计或增加输出清单的情况。
优点:
与
istioctl install相同的 API,但通过集群中的控制器 Pod 进行操作,实现了完全声明式操作。IstioOperator API提供了广泛的配置/定制选项。不需要管理多个
istioctl二进制文件。
缺点:
- 集群中运行的高权限控制器存在安全风险。
安装 Istio
==🚩 实战:istioctl 方式安装istio-2023.11.3(测试成功)==
实验环境:
k8s v1.25.4(containerd://1.6.10)
[root@master1 ~]#istioctl version
client version: 1.19.3
control plane version: 1.19.3
data plane version: 1.19.3 (8 proxies)实验软件:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pMnJxgL63oTlGFlhrfnXsA?pwd=7yqb 提取码:7yqb 2023.11.5-实战:BookInfo 示例应用-2023.11.5(测试成功) (使用的是同一个软件包)
上面我们对几种方式做了简单的对比,具体选择哪种方式安装需要结合自己的情况来决定。我们这里就选择社区推荐的 istioctl 方式进行安装。
首先前往 Istio Release 页面下载适合你操作系统的安装文件,或使用下面的命令自动下载并解压最新版本(Linux 或 macOS):
curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | sh -#!/bin/sh
# Copyright Istio Authors
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
#
# This file will be fetched as: curl -L https://git.io/getLatestIstio | sh -
# so it should be pure bourne shell, not bash (and not reference other scripts)
#
# The script fetches the latest Istio release candidate and untars it.
# You can pass variables on the command line to download a specific version
# or to override the processor architecture. For example, to download
# Istio 1.6.8 for the x86_64 architecture and linux OS,
# run curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=1.6.8 TARGET_ARCH=x86_64 TARGET_OS=Linux sh -.
set -e
# Determines the operating system.
OS="${TARGET_OS:-$(uname)}"
if [ "${OS}" = "Darwin" ] ; then
OSEXT="osx"
else
OSEXT="linux"
fi
# Determine the latest Istio version by version number ignoring alpha, beta, and rc versions.
if [ "${ISTIO_VERSION}" = "" ] ; then
ISTIO_VERSION="$(curl -sL https://github.com/istio/istio/releases | \
grep -o 'releases/[0-9]*.[0-9]*.[0-9]*/' | sort -V | \
tail -1 | awk -F'/' '{ print $2}')"
ISTIO_VERSION="${ISTIO_VERSION##*/}"
fi
LOCAL_ARCH=$(uname -m)
if [ "${TARGET_ARCH}" ]; then
LOCAL_ARCH=${TARGET_ARCH}
fi
case "${LOCAL_ARCH}" in
x86_64|amd64)
ISTIO_ARCH=amd64
;;
armv8*|aarch64*|arm64)
ISTIO_ARCH=arm64
;;
armv*)
ISTIO_ARCH=armv7
;;
*)
echo "This system's architecture, ${LOCAL_ARCH}, isn't supported"
exit 1
;;
esac
if [ "${ISTIO_VERSION}" = "" ] ; then
printf "Unable to get latest Istio version. Set ISTIO_VERSION env var and re-run. For example: export ISTIO_VERSION=1.0.4"
exit 1;
fi
NAME="istio-$ISTIO_VERSION"
URL="https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/${ISTIO_VERSION}/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}-${OSEXT}.tar.gz"
ARCH_URL="https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/${ISTIO_VERSION}/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}-${OSEXT}-${ISTIO_ARCH}.tar.gz"
with_arch() {
printf "\nDownloading %s from %s ...\n" "$NAME" "$ARCH_URL"
if ! curl -o /dev/null -sIf "$ARCH_URL"; then
printf "\n%s is not found, please specify a valid ISTIO_VERSION and TARGET_ARCH\n" "$ARCH_URL"
exit 1
fi
curl -fsLO "$ARCH_URL"
filename="istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}-${OSEXT}-${ISTIO_ARCH}.tar.gz"
tar -xzf "${filename}"
rm "${filename}"
}
without_arch() {
printf "\nDownloading %s from %s ..." "$NAME" "$URL"
if ! curl -o /dev/null -sIf "$URL"; then
printf "\n%s is not found, please specify a valid ISTIO_VERSION\n" "$URL"
exit 1
fi
curl -fsLO "$URL"
filename="istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}-${OSEXT}.tar.gz"
tar -xzf "${filename}"
rm "${filename}"
}
# Istio 1.6 and above support arch
# Istio 1.5 and below do not have arch support
ARCH_SUPPORTED="1.6"
# Istio 1.10 and above support arch for osx arm64
ARCH_SUPPORTED_OSX="1.10"
if [ "${OS}" = "Linux" ] ; then
# This checks if ISTIO_VERSION is less than ARCH_SUPPORTED (version-sort's before it)
if [ "$(printf '%s\n%s' "${ARCH_SUPPORTED}" "${ISTIO_VERSION}" | sort -V | head -n 1)" = "${ISTIO_VERSION}" ]; then
without_arch
else
with_arch
fi
elif [ "${OS}" = "Darwin" ] ; then
# This checks if ISTIO_VERSION is less than ARCH_SUPPORTED_OSX (version-sort's before it) or ISTIO_ARCH not equal to arm64
if [ "$(printf '%s\n%s' "${ARCH_SUPPORTED_OSX}" "${ISTIO_VERSION}" | sort -V | head -n 1)" = "${ISTIO_VERSION}" ] || [ "${ISTIO_ARCH}" != "arm64" ]; then
without_arch
else
with_arch
fi
else
printf "\n\n"
printf "Unable to download Istio %s at this moment!\n" "$ISTIO_VERSION"
printf "Please verify the version you are trying to download.\n\n"
exit 1
fi
printf ""
printf "\nIstio %s Download Complete!\n" "$ISTIO_VERSION"
printf "\n"
printf "Istio has been successfully downloaded into the %s folder on your system.\n" "$NAME"
printf "\n"
BINDIR="$(cd "$NAME/bin" && pwd)"
printf "Next Steps:\n"
printf "See https://istio.io/latest/docs/setup/install/ to add Istio to your Kubernetes cluster.\n"
printf "\n"
printf "To configure the istioctl client tool for your workstation,\n"
printf "add the %s directory to your environment path variable with:\n" "$BINDIR"
printf "\t export PATH=\"\$PATH:%s\"\n" "$BINDIR"
printf "\n"
printf "Begin the Istio pre-installation check by running:\n"
printf "\t istioctl x precheck \n"
printf "\n"
printf "Need more information? Visit https://istio.io/latest/docs/setup/install/ \n"
🍀
但是上面方式默认也是走 github 下载,国内访问 github 速度比较慢(也可能根本下载不了),所有我们可以自己去下载安装文件包,下载完成后解压,将解压后的 istioctl 文件移动到 /usr/local/bin 目录下:
# wget https://ghps.cc/https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/1.19.3/istio-1.19.3-linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ wget https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/1.19.3/istio-1.19.3-linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ tar -xvf istio-1.19.3-linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ mv istio-1.19.3/bin/istioctl /usr/local/bin/
$ istioctl version
no ready Istio pods in "istio-system"
1.19.3能执行 istioctl 命令说明安装成功,但是提示 no ready Istio pods in "istio-system",这是因为我们还没有安装 Istio,接下来我们就来安装 Istio。

istioctl 工具中内置了一些安装配置文件,这些配置文件提供了对 Istio 控制平面和 Istio 数据平面 Sidecar 的定制内容。我们可以通过 istioctl profile list 命令查看:
$ istioctl profile list
Istio configuration profiles:
ambient
default
demo
empty
external
minimal
openshift
preview
remote我们可以从其中一个 Istio 内置配置文件开始入手, 然后根据特定需求进一步自定义配置文件。
default:根据IstioOperator API的默认配置启动组件。建议将此配置文件用于生产部署和多集群网格中的主集群,我们可以运行istioctl profile dump命令来查看默认设置,如下所示其实就是一个IstioOperator的配置文件:
注意:这里的IstioOperator和我们之前k8s里Operator不一样,这里没有直接的控制器,它是通过istioctl命令来做的一些解析。
istioctl 能够识别的一个安装配置文件,只是这个配置文件采用了类似于K8s CRD的方式来声明而已,并没有对应的控制器Pod。
#istioctl profile dump default
$ istioctl profile dump
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:
components:
base:
enabled: true
cni:
enabled: false
egressGateways:
- enabled: false
name: istio-egressgateway
ingressGateways:
- enabled: true
name: istio-ingressgateway
istiodRemote:
enabled: false
pilot:
enabled: true
hub: docker.io/istio
meshConfig:
defaultConfig:
proxyMetadata: {}
enablePrometheusMerge: true
profile: default
tag: 1.19.3
values:
base:
enableCRDTemplates: false
validationURL: ""
defaultRevision: ""
gateways:
istio-egressgateway:
autoscaleEnabled: true
env: {}
name: istio-egressgateway
secretVolumes:
- mountPath: /etc/istio/egressgateway-certs
name: egressgateway-certs
secretName: istio-egressgateway-certs
- mountPath: /etc/istio/egressgateway-ca-certs
name: egressgateway-ca-certs
secretName: istio-egressgateway-ca-certs
type: ClusterIP
istio-ingressgateway:
autoscaleEnabled: true
env: {}
name: istio-ingressgateway
secretVolumes:
- mountPath: /etc/istio/ingressgateway-certs
name: ingressgateway-certs
secretName: istio-ingressgateway-certs
- mountPath: /etc/istio/ingressgateway-ca-certs
name: ingressgateway-ca-certs
secretName: istio-ingressgateway-ca-certs
type: LoadBalancer
global:
configValidation: true
defaultNodeSelector: {}
defaultPodDisruptionBudget:
enabled: true
defaultResources:
requests:
cpu: 10m
imagePullPolicy: ""
imagePullSecrets: []
istioNamespace: istio-system
istiod:
enableAnalysis: false
jwtPolicy: third-party-jwt
logAsJson: false
logging:
level: default:info
meshNetworks: {}
mountMtlsCerts: false
multiCluster:
clusterName: ""
enabled: false
network: ""
omitSidecarInjectorConfigMap: false
oneNamespace: false
operatorManageWebhooks: false
pilotCertProvider: istiod
priorityClassName: ""
proxy:
autoInject: enabled
clusterDomain: cluster.local
componentLogLevel: misc:error
enableCoreDump: false
excludeIPRanges: ""
excludeInboundPorts: ""
excludeOutboundPorts: ""
image: proxyv2
includeIPRanges: '*'
logLevel: warning
privileged: false
readinessFailureThreshold: 30
readinessInitialDelaySeconds: 1
readinessPeriodSeconds: 2
resources:
limits:
cpu: 2000m
memory: 1024Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
statusPort: 15020
tracer: zipkin
proxy_init:
image: proxyv2
sds:
token:
aud: istio-ca
sts:
servicePort: 0
tracer:
datadog: {}
lightstep: {}
stackdriver: {}
zipkin: {}
useMCP: false
istiodRemote:
injectionURL: ""
pilot:
autoscaleEnabled: true
autoscaleMax: 5
autoscaleMin: 1
configMap: true
cpu:
targetAverageUtilization: 80
env: {}
image: pilot
keepaliveMaxServerConnectionAge: 30m
nodeSelector: {}
podLabels: {}
replicaCount: 1
traceSampling: 1
telemetry:
enabled: true
v2:
enabled: true
metadataExchange:
wasmEnabled: false
prometheus:
enabled: true
wasmEnabled: false
stackdriver:
configOverride: {}
enabled: false
logging: false
monitoring: false
topology: falsedemo:这个配置旨在展示 Istio 功能,具有适度的资源要求。它适合运行官方的 Bookinfo 示例应用和相关任务,比较适合用于快速入门的安装配置,比如我们这里就可以使用该配置。此配置文件启用了高级别的追踪和访问日志,因此不适合进行性能测试。我们也可以使用istioctl profile dump demo命令来查看该配置文件的具体配置资源对象。minimal:与默认配置文件相同,但只安装了控制平面组件。这样我们就可以使用单独的配置文件来配置控制平面和数据平面组件(例如网关)。remote:用于配置一个远程集群, 这个从集群由外部控制平面管理, 或者由多集群网格的主集群中的控制平面管理。empty:不部署任何内容,可以作为自定义配置的基本配置文件。preview:预览文件包含的功能都属于实验性阶段。该配置文件是为了探索 Istio 的新功能。确保稳定性、安全性和性能(使用风险需自负)。ambient:Ambient 配置文件用于帮助开始使用Ambient Mesh。需要注意的是 Ambient 目前处于 Alpha 状态。请勿在生产环境中使用 Ambient 模式。openshift:用于在 OpenShift 上安装 Istio。
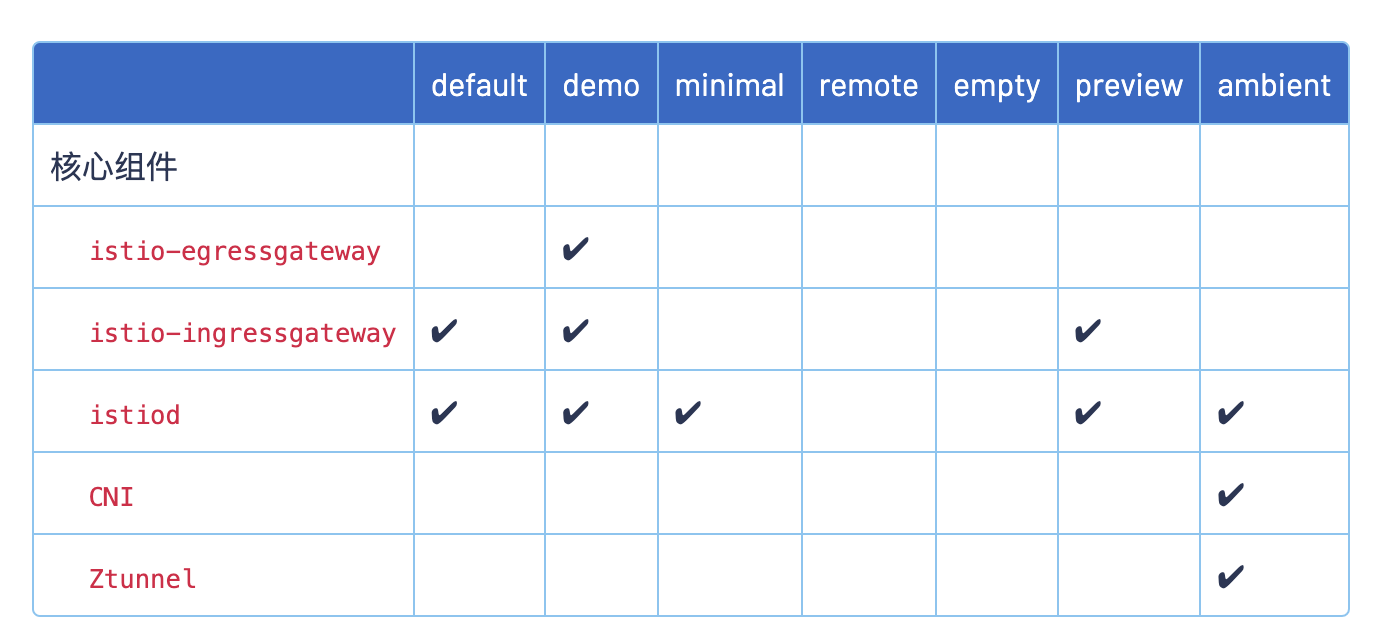
标注 ✔ 的组件安装在每个配置文件中:
除了安装 Istio 内置的配置之外,istioctl install 还提供了一套完整的用于定制配置的 API - IstioOperator API。
此 API 中的配置参数可以使用命令行选项 --set 进行独立设置,比如要在 default 配置中启动 debug 的日志特性,我们可以使用下面的命令:
$ istioctl install --set values.global.logging.level=debug或者,可以在 YAML 文件中指定 IstioOperator 的配置,然后用 -f 选项传递给 istioctl 即可:
$ istioctl install -f samples/operator/pilot-k8s.yamlIstioOperator API 定义主要包括如下几个组件:
basepilotingressGatewaysegressGatewayscniistiodRemote
针对每一个组件的配置内容通过 components.<component name> 下的 API 中提供。例如,要用 API 更改 pilot 组件的 enabled 设置, 可以使用 --set components.pilot.enabled=false 命令,或在 IstioOperator 资源中设置:
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:
components:
pilot:
enabled: false这样安装后就不会启动 pilot 组件了。
所有的组件共享一个通用 API,用来修改 Kubernetes 特定的设置,它在 components.<component name>.k8s 路径下,它允许修改如下设置:
- Resources
- Readiness probes
- Replica count
- HorizontalPodAutoscaler
- PodDisruptionBudget
- Pod annotations
- Service annotations
- ImagePullPolicy
- Priority class name
- Node selector
- Affinity and anti-affinity
- Service
- Toleration
- Strategy
- Env
- Pod security context
所有这些 Kubernetes 设置也就是平时我们使用的 Kubernetes API 定义,配置方式完全一样。比如我们要调整 Pilot 组件的资源限制和 Pod 水平伸缩,可以用如下所示的配置:
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
spec:
components:
pilot:
k8s:
resources:
requests:
cpu: 1000m # 覆盖默认的 500m
memory: 4096Mi # ... 默认 2048Mi
hpaSpec:
maxReplicas: 10 # ... 默认 5
minReplicas: 2 # ... 默认 1然后我们就可以直接使用 istioctl install 把改变的设置应用到集群:
$ istioctl install -f samples/operator/pilot-k8s.yaml🍀
了解了 Istio 安装的基本概念之后,我们就可以开始安装 Istio 了,我们这里选择 demo 配置文件进行安装,选择它是因为它包含了一组专为测试准备的功能集合,另外还有用于生产或性能测试的配置组合。
执行下面的命令即可:
$ istioctl install --set profile=demo -y
✔ Istio core installed
✔ Istiod installed
✔ Egress gateways installed
✔ Ingress gateways installed
✔ Installation complete
Made this installation the default for injection and validation.可以看到上面的 demo 配置应用后,启用了 Istio core、Istiod、Egress gateways、Ingress gateways 几个组件,这些组件都是通过 IstioOperator API 进行配置的。
🍀
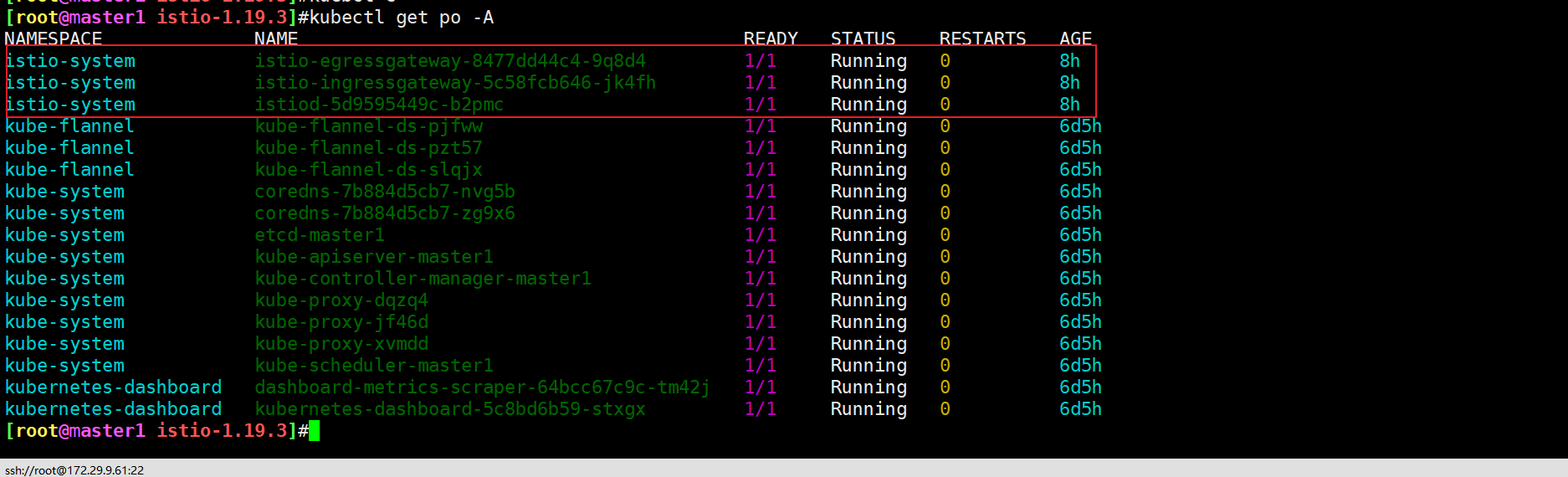
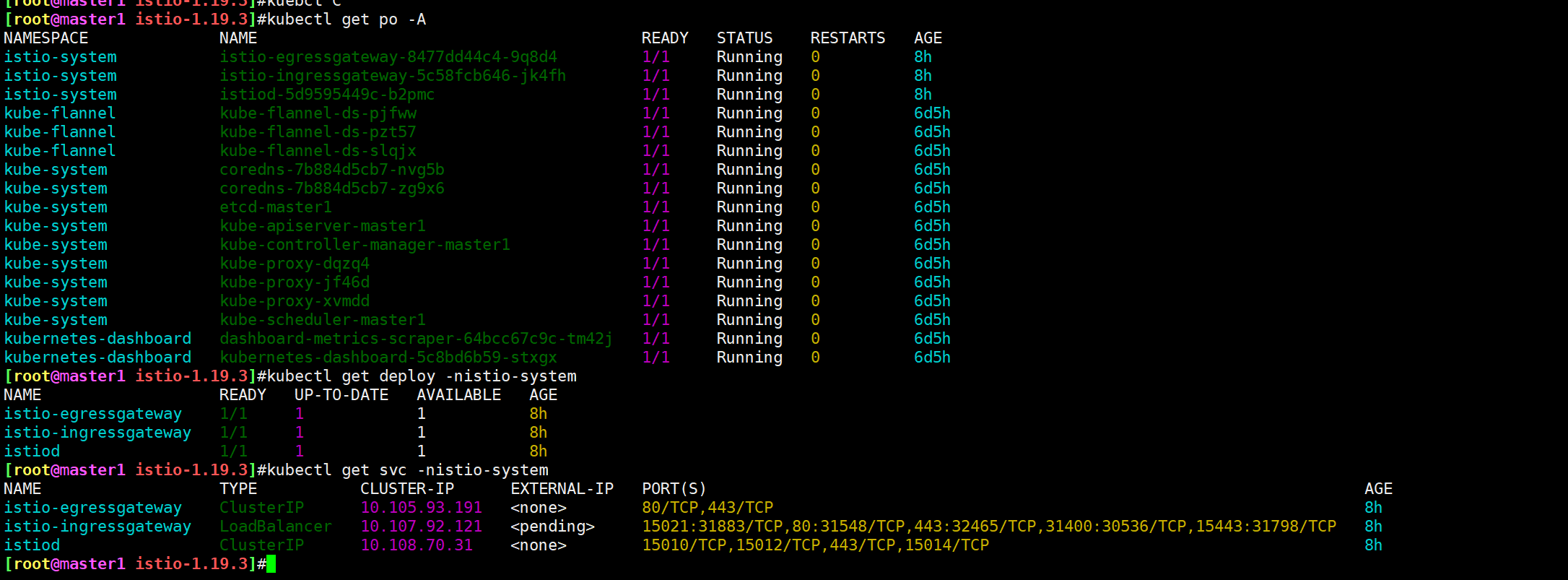
安装完成后会自动创建一个 istio-system 命名空间,包含如下几个 Pod,分别对应上面的几个组件:
[root@master1 ~]#kubectl get po -nistio-system
这其实也和 Istio 架构中的组件是一一对应的,我们可以再看下 Istio 架构图:

istio-egressgateway:出口网关,用于处理出站流量。istio-ingressgateway:入口网关,用于处理入站流量,接收传入的 HTTP/TCP 连接。istiod:Istio 控制平面,用于管理和配置数据平面,提供服务网格的核心功能。
当然安装后并没有出现架构图上面的数据平面相关组件,这是因为数据平面的 Envoy Sidecar 代理是伴随应用 Pod 一起的,所以需要部署应用后才会出现。
安装成功。😘
2、注入 Envoy Sidecar
要为应用注入 Envoy Sidecar 代理有几种方法:
1.手动注入 Sidecar
==🚩 实战:手动注入 Envoy Sidecar-2023.11.3(测试成功)==
实验环境:
k8s v1.25.4(containerd://1.6.10)
[root@master1 ~]#istioctl version
client version: 1.19.3
control plane version: 1.19.3
data plane version: 1.19.3 (8 proxies)实验软件:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pMnJxgL63oTlGFlhrfnXsA?pwd=7yqb 提取码:7yqb 2023.11.5-实战:BookInfo 示例应用-2023.11.5(测试成功) (使用的是同一个软件包)

默认的测试demo如下位置:
[root@master1 ~]#cat istio-1.19.3/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
# Copyright Istio Authors
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
##################################################################################################
# Sleep service
##################################################################################################
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: sleep
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: sleep
labels:
app: sleep
service: sleep
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: http
selector:
app: sleep
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: sleep
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: sleep
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: sleep
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
serviceAccountName: sleep
containers:
- name: sleep
image: curlimages/curl
command: ["/bin/sleep", "infinity"]
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/sleep/tls
name: secret-volume
volumes:
- name: secret-volume
secret:
secretName: sleep-secret
optional: true
---
[root@master1 ~]#🍀
先来部署这个应用
[root@master1 ~]#kubectl apply -f istio-1.19.3/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
serviceaccount/sleep created
service/sleep created
deployment.apps/sleep created
[root@master1 ~]#kubectl get po -l app=sleep
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-78ff5975c6-ftlzx 1/1 Running 0 46s这是一个正常应用的状态。
🍀
比如我们为一个 Deployment 手动注入 Sidecar,可以使用下面的方法:
# istio-1.19.3 目录下
$ istioctl kube-inject -f samples/sleep/sleep.yaml | kubectl apply -f -
serviceaccount/sleep created
service/sleep created
deployment.apps/sleep created
默认情况下 Pod 的注入是基于 Sidecar 注入模板,在 istio-sidecar-injector Configmap 中配置,我们可以将配置导出到本地,然后手动指定注入也可以:
$ kubectl -n istio-system get configmap istio-sidecar-injector -o=jsonpath='{.data.config}' > inject-config.yaml
$ kubectl -n istio-system get configmap istio-sidecar-injector -o=jsonpath='{.data.values}' > inject-values.yaml
$ kubectl -n istio-system get configmap istio -o=jsonpath='{.data.mesh}' > mesh-config.yaml然后指定输入文件,运行 kube-inject 并部署应用即可:
$ istioctl kube-inject \
--injectConfigFile inject-config.yaml \
--meshConfigFile mesh-config.yaml \
--valuesFile inject-values.yaml \
--filename samples/sleep/sleep.yaml \
| kubectl apply -f -🍀
正常部署后我们的应用 Pod 中会多出一个 Sidecar 容器:
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get po -l app=sleep
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-7cbcd885cf-6j4bt 2/2 Running 0 2m8s
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#这个容器就是 Envoy Sidecar 代理。

这个 Envoy Sidecar 代理,它会和应用 Pod 一起运行,用来代理整个应用的流量,当然整体控制都是由 Istio 控制平面来决定的。而 Istio 控制平面实现了 Envoy 的控制平面接口,可以动态下发修改 Envoy 的配置,这样我们就可以去操控这些 Envoy Sidecar 了,这是不是和我们前面讲解的 Envoy 基于 API 的动态配置部分就关联起来了,所以我们说需要先熟悉 Envoy,然后再来学习 Istio 效果会更好。
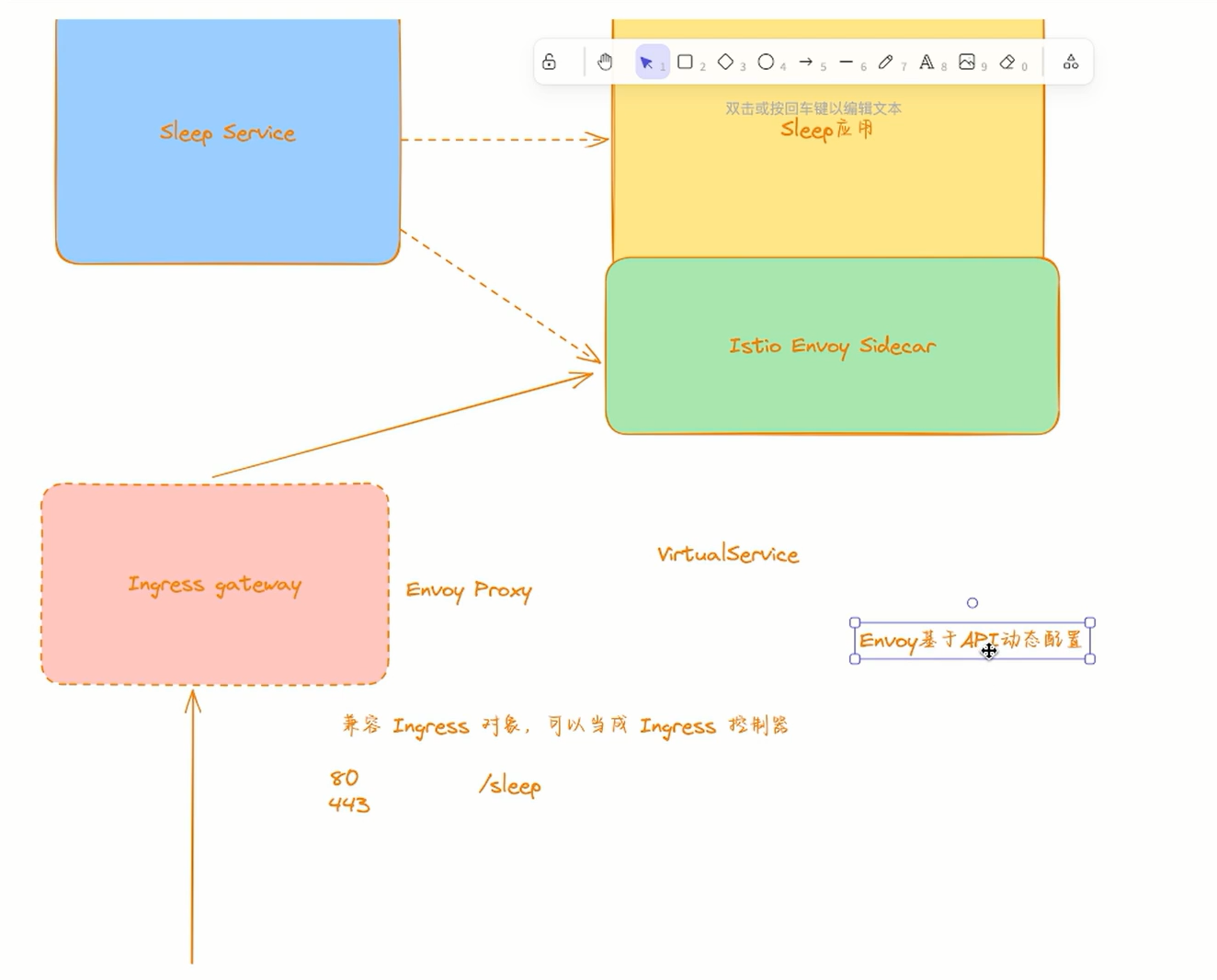
🍀
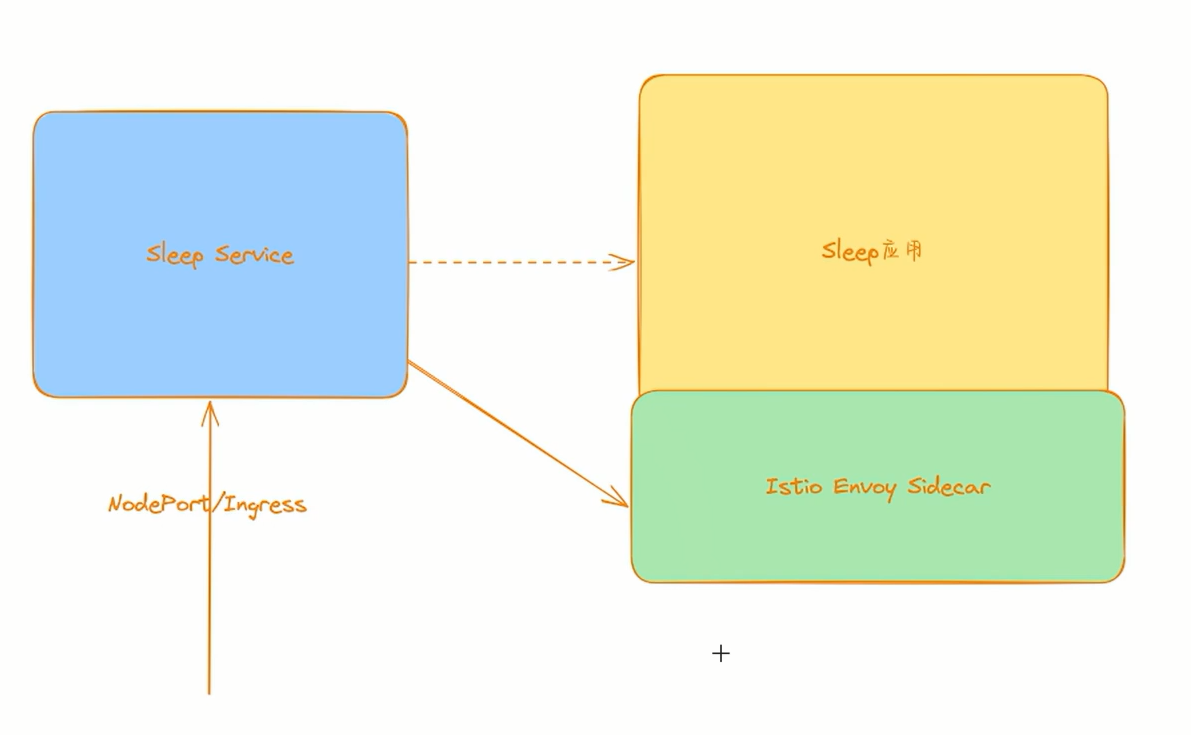
测试完成。😘
2.自定义注入
上面我们了解到 Pod 的注入是基于 istio-sidecar-injector 这个 Configmap 模板的,同样的我们也可以自行定义注入 Sidecar 代理。我们可以通过在 Pod 中手动添加一个 istio-proxy 容器来完成,Sidecar 注入将会把自定义的任何配置视为默认注入模板的覆盖。
自定义这些设置时,需格外小心,因为允许完全自定义生成的 Pod,包括进行一些更改而导致 Sidecar 容器无法正常运行。
例如,以下配置可自定义各种设置,包括降低 CPU 请求,添加 Volume 挂载,和添加 preStop Hook:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: example
spec:
containers:
- name: hello
image: alpine
- name: istio-proxy # 这个容器名需要叫 istio-proxy
image: auto # 设置为 auto,自动选择要使用的 Image
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /etc/certs
name: certs
lifecycle:
preStop:
exec:
command: ["sleep", "10"]
volumes:
- name: certs
secret:
secretName: istio-certs一般来说 Pod 中的任何字段我们都可以配置,但是必须注意某些字段:
- Kubernetes 要求在注入运行之前配置 image,虽然可以可以设置一个指定的 Image 来覆盖默认的 image 配置,但建议将 image 设置为
auto,可使 Sidecar 注入自动选择要使用的 Image。 - Pod 中一些字段取决于相关设置。例如,CPU 请求必须小于 CPU 限制。
3.自动注入 Sidecar
==🚩 实战:自动注入 Envoy Sidecar-2023.11.8(测试成功)==
实验环境:
k8s v1.27.6(containerd://1.6.20)
[root@master1 ~]#istioctl version
client version: 1.19.3
control plane version: 1.19.3
data plane version: 1.19.3 (8 proxies)实验软件:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pMnJxgL63oTlGFlhrfnXsA?pwd=7yqb 提取码:7yqb 2023.11.5-实战:BookInfo 示例应用-2023.11.5(测试成功) (使用的是同一个软件包)

上面我们介绍了手动注入和自定义注入两种方式,这些都是需要我们手动去操作的,此外我们也可以通过配置实现自动注入,这样我们就不需要手动去注入了,Istio 提供了一个 Kubernetes 准入控制器,它可以自动注入 Sidecar 代理,我们只需要为命名空间设置 istio-injection=enabled 标签即可启用自动注入。
🍀
比如我们先在集群中部署 sleep 应用:(测试之前记得先删除先前的测试demo)
#在目录istio-1.19.3下
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl apply -f samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
serviceaccount/sleep unchanged
service/sleep unchanged
deployment.apps/sleep created
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get deploy
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
sleep 1/1 1 1 22s
web 1/1 1 1 6d4h
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get pod -l app=sleep
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-78ff5975c6-v62sv 1/1 Running 0 31s目前我们的 sleep 应用是没有注入 Sidecar 的,只有 1 个容器。
🍀
现在我们可以为 default 命名空间打上 istio-injection=enabled 标签:
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled --overwrite
namespace/default labeled
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get namespace -L istio-injection
NAME STATUS AGE ISTIO-INJECTION
default Active 6d4h enabled
istio-system Active 8h
kube-flannel Active 6d4h
kube-node-lease Active 6d4h
kube-public Active 6d4h
kube-system Active 6d4h
kubernetes-dashboard Active 6d4h
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get pod -l app=sleep
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-78ff5975c6-v62sv 1/1 Running 0 108s🍀
现在我们为命名空间打上了自动注入标签,但是已经部署了的应用并不会主动注入,这是因为注入的动作发生着 Pod 创建时。我们可以杀掉正在运行的 Pod 来验证新创建的 Pod 是否注入 Sidecar。
$ kubectl delete pod -l app=sleep
$ kubectl get pod -l app=sleep
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-9454cc476-kmbzz 2/2 Running 0 5s可以看到现在我们的应用有 2 个容器了。查看已注入 Pod 的详细状态,应该可以看到被注入的 istio-proxy 容器:
$ kubectl describe pod -l app=sleep
...
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 91s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/sleep-9454cc476-kmbzz to node2
Normal Pulled 90s kubelet Container image "docker.io/istio/proxyv2:1.19.3" already present on machine
Normal Created 90s kubelet Created container istio-init
Normal Started 90s kubelet Started container istio-init
Normal Pulled 90s kubelet Container image "curlimages/curl" already present on machine
Normal Created 90s kubelet Created container sleep
Normal Started 90s kubelet Started container sleep
Normal Pulled 90s kubelet Container image "docker.io/istio/proxyv2:1.19.3" already present on machine
Normal Created 89s kubelet Created container istio-proxy
Normal Started 89s kubelet Started container istio-proxy这样我们就实现了 Pod 应用自动注入 Envoy Sidecar 代理,以后 default 命名空间中的应用部署后都会自动注入了。当然要取消自动注入功能,只需要将 istio-injection 标签去掉即可:
$ kubectl label namespace default istio-injection-当然除了在命名空间级别启用和禁用注入功能之外,注入也可以通过配置 Pod 上的 sidecar.istio.io/inject: "true" 标签,在每个 Pod 的基础上进行控制。
自动注入 Envoy Sidecar 的原理其实很简单,如果你对 Kubernetes 比较熟悉的话,肯定听过准入控制器的,其中就有两个对象 validatingwebhookconfigurations、mutatingwebhookconfigurations,前面是用来校验资源是否合法的,后面是用来修改资源对象的,那么要实现自动注入功能,也就相当于去为 Pod 自动添加一个容器,所以就需要用到 mutate 功能了,我们可以查看下系统中是否包含一个 istio-sidecar-injector 的准入控制器:
$ kubectl get mutatingwebhookconfigurations
NAME WEBHOOKS AGE
istio-sidecar-injector 4 63m而实现准入控制器逻辑的也正是 istiod 这个组件了。

⚠️
==但是特别注意:我这里在做测试时出现了问题。。。排查了好多次,有点浪费时间。。。==
- 但是,我这里出现问题了。。。提示:创建pod失败,内部错误发生,失败调用webhook……
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get po
No resources found in default namespace.
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get deploy sleep
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
sleep 0/1 0 0 8m32s
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl describe deployments.apps sleep
Name: sleep
Namespace: default
CreationTimestamp: Fri, 03 Nov 2023 21:50:31 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1
Selector: app=sleep
Replicas: 1 desired | 0 updated | 0 total | 0 available | 1 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 25% max unavailable, 25% max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: app=sleep
Service Account: sleep
Containers:
sleep:
Image: curlimages/curl
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Command:
/bin/sleep
infinity
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/etc/sleep/tls from secret-volume (rw)
Volumes:
secret-volume:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: sleep-secret
Optional: true
Conditions:
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable
Available False MinimumReplicasUnavailable
ReplicaFailure True FailedCreate
OldReplicaSets: <none>
NewReplicaSet: sleep-78ff5975c6 (0/1 replicas created)
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal ScalingReplicaSet 8m39s deployment-controller Scaled up replica set sleep-78ff5975c6 to 1
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#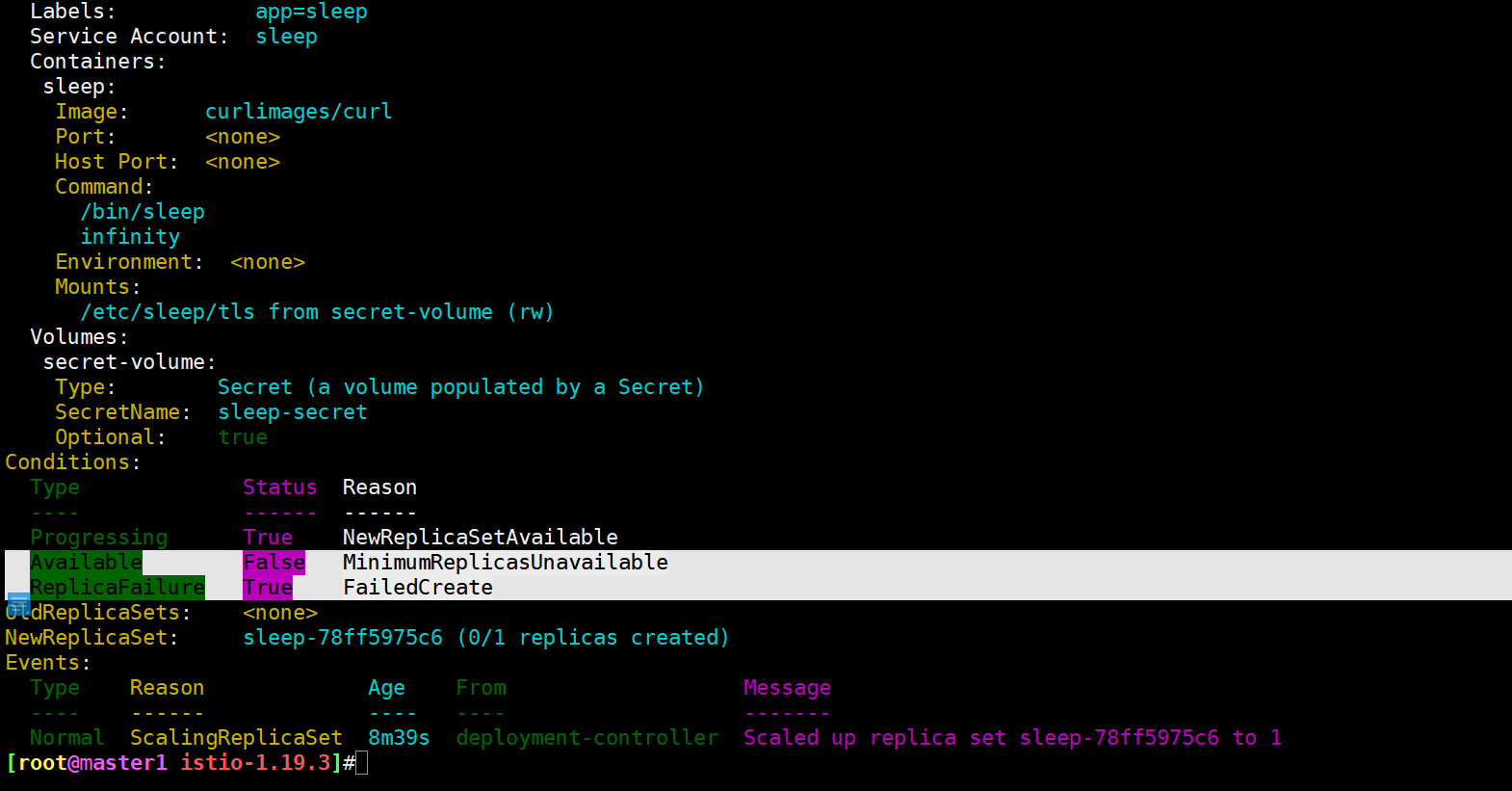
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get rs sleep-78ff5975c6
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
sleep-78ff5975c6 1 0 0 10m
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl describe rs sleep-78ff5975c6
Name: sleep-78ff5975c6
Namespace: default
Selector: app=sleep,pod-template-hash=78ff5975c6
Labels: app=sleep
pod-template-hash=78ff5975c6
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/desired-replicas: 1
deployment.kubernetes.io/max-replicas: 2
deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1
Controlled By: Deployment/sleep
Replicas: 0 current / 1 desired
Pods Status: 0 Running / 0 Waiting / 0 Succeeded / 0 Failed
Pod Template:
Labels: app=sleep
pod-template-hash=78ff5975c6
Service Account: sleep
Containers:
sleep:
Image: curlimages/curl
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Command:
/bin/sleep
infinity
Environment: <none>
Mounts:
/etc/sleep/tls from secret-volume (rw)
Volumes:
secret-volume:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: sleep-secret
Optional: true
Conditions:
Type Status Reason
---- ------ ------
ReplicaFailure True FailedCreate
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal SuccessfulCreate 10m replicaset-controller Created pod: sleep-78ff5975c6-9tpms
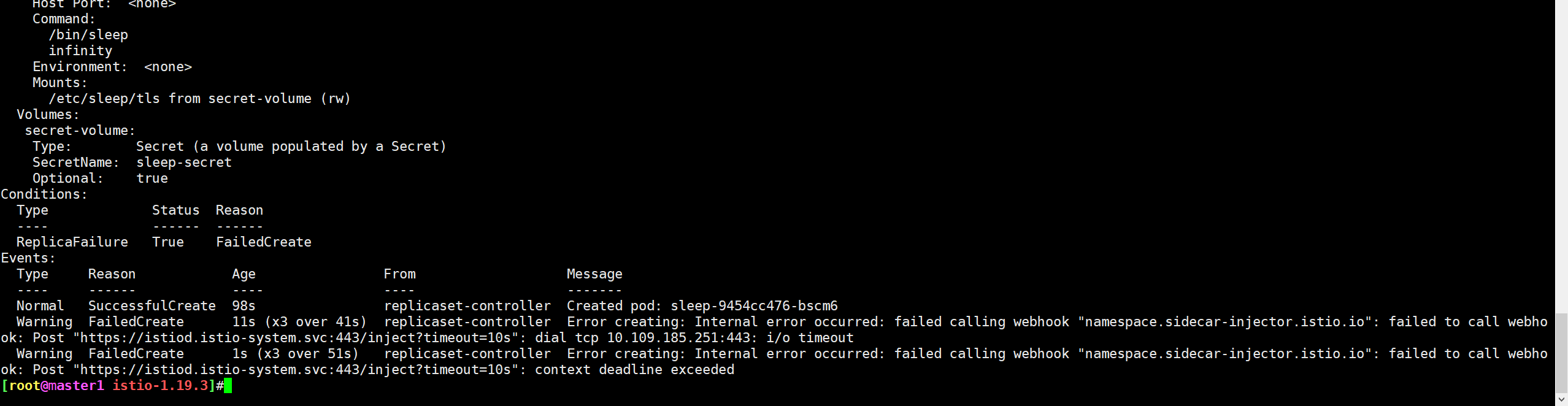
Warning FailedCreate 6m58s (x4 over 8m58s) replicaset-controller Error creating: Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "namespace.sidecar-injector.istio.io": failed to call webhook: Post "https://istiod.istio-system.svc:443/inject?timeout=10s": dial tcp 10.108.70.31:443: i/o timeout
Warning FailedCreate 101s (x13 over 9m8s) replicaset-controller Error creating: Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "namespace.sidecar-injector.istio.io": failed to call webhook: Post "https://istiod.istio-system.svc:443/inject?timeout=10s": context deadline exceeded
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#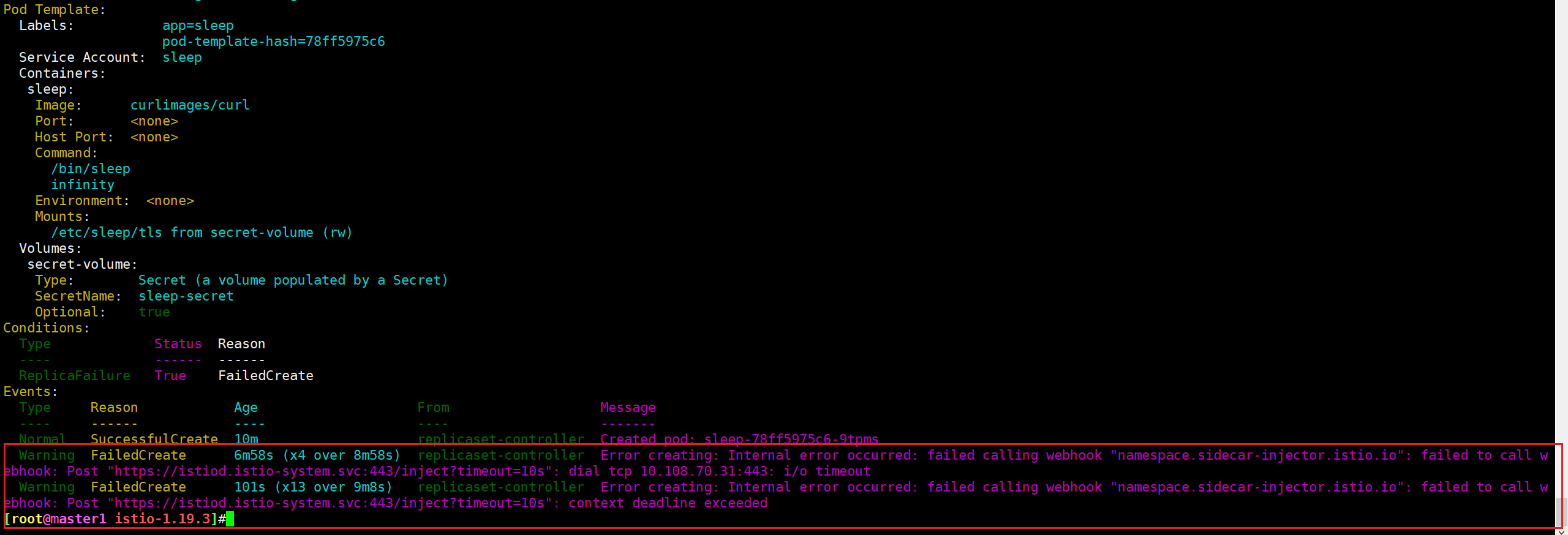
提示:创建pod失败,内部错误发生,失败调用webhook……

奇怪。。。。
老师的都没问题。。。
重启istio组件测试(失败)
重启k8s集群(失败)
- istiod日志
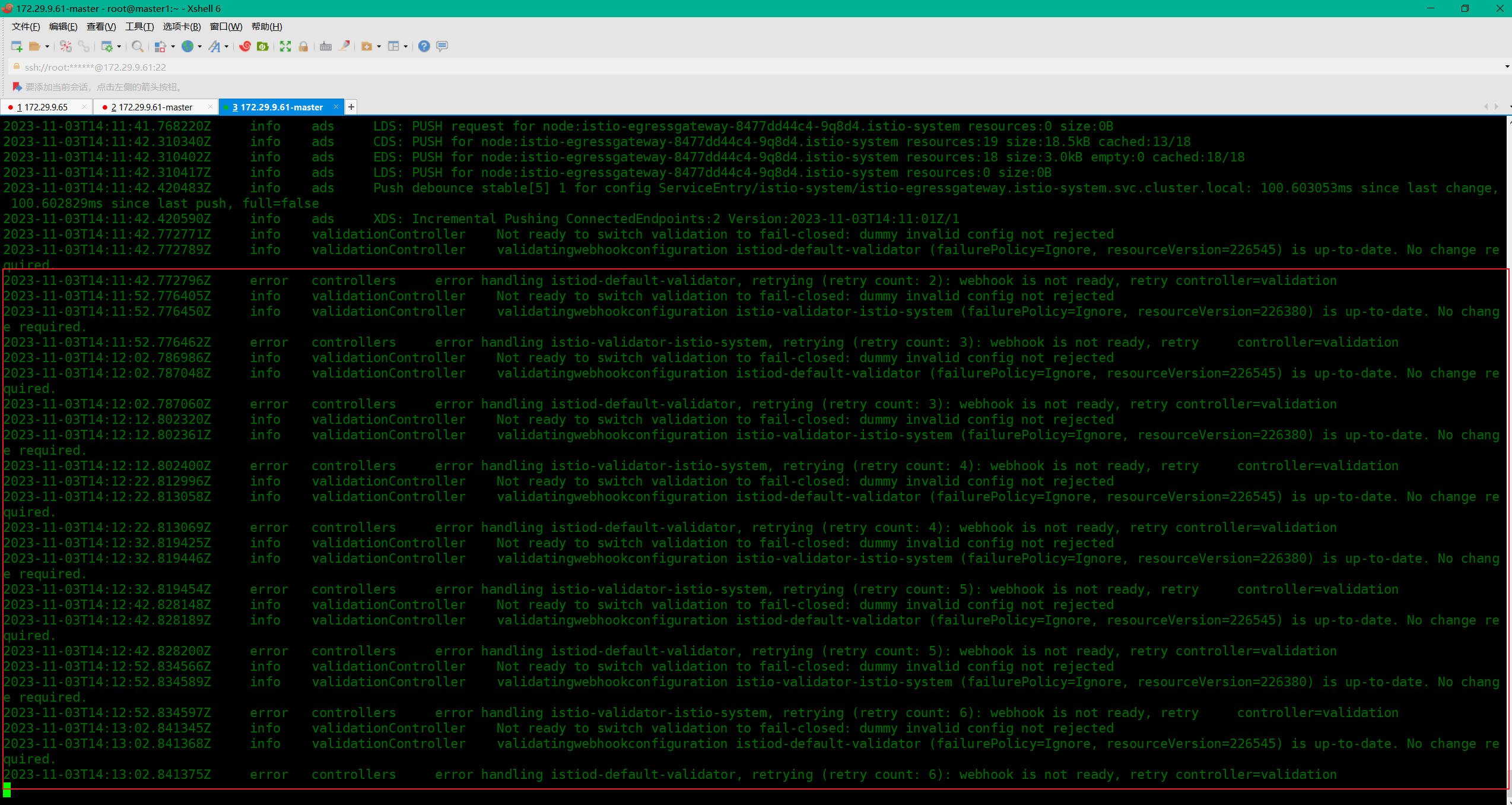
- 个人判断是自己的k8s集群版与老师集群版本不一致或需要开启什么webhook等……
很大程度是这个问题导致的。。。
老师环境:

自己环境:


删除istiod,重装还是有问题。。。
后期重新搭建了v1.27.6版本k8s集群测试,containerd v1.6.20,但是还是不行。。。
重装完成k8s后,还是无法自动注入哇。。。。
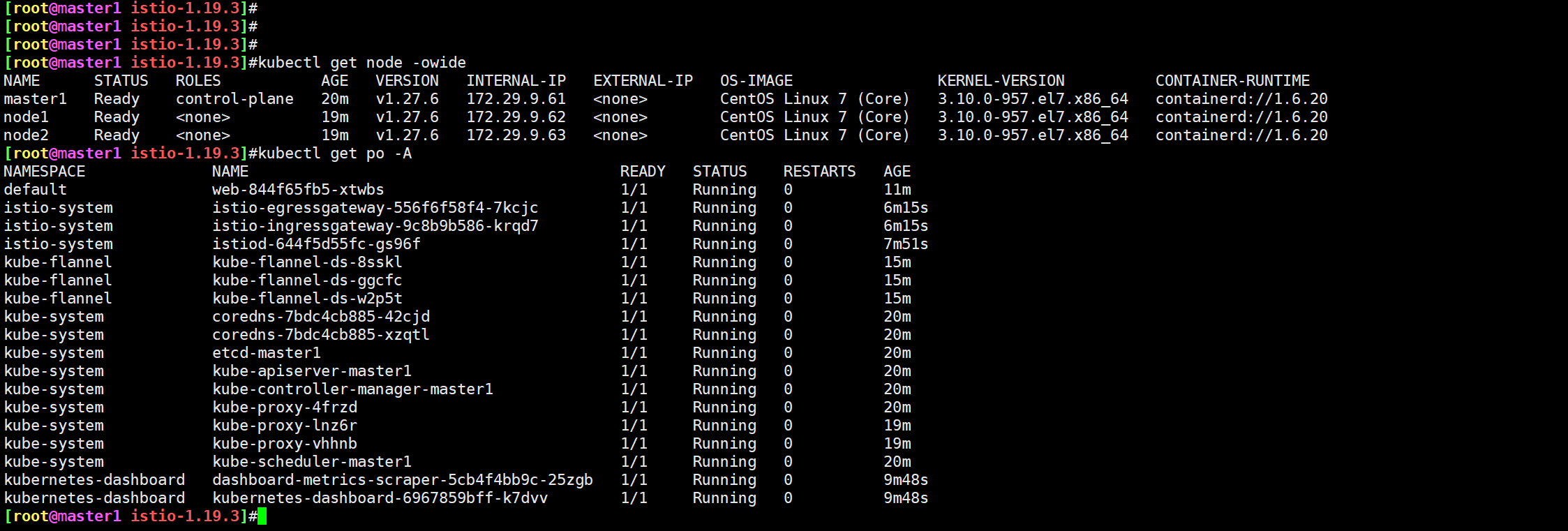
istiod-644f5d55fc-gs96f日志
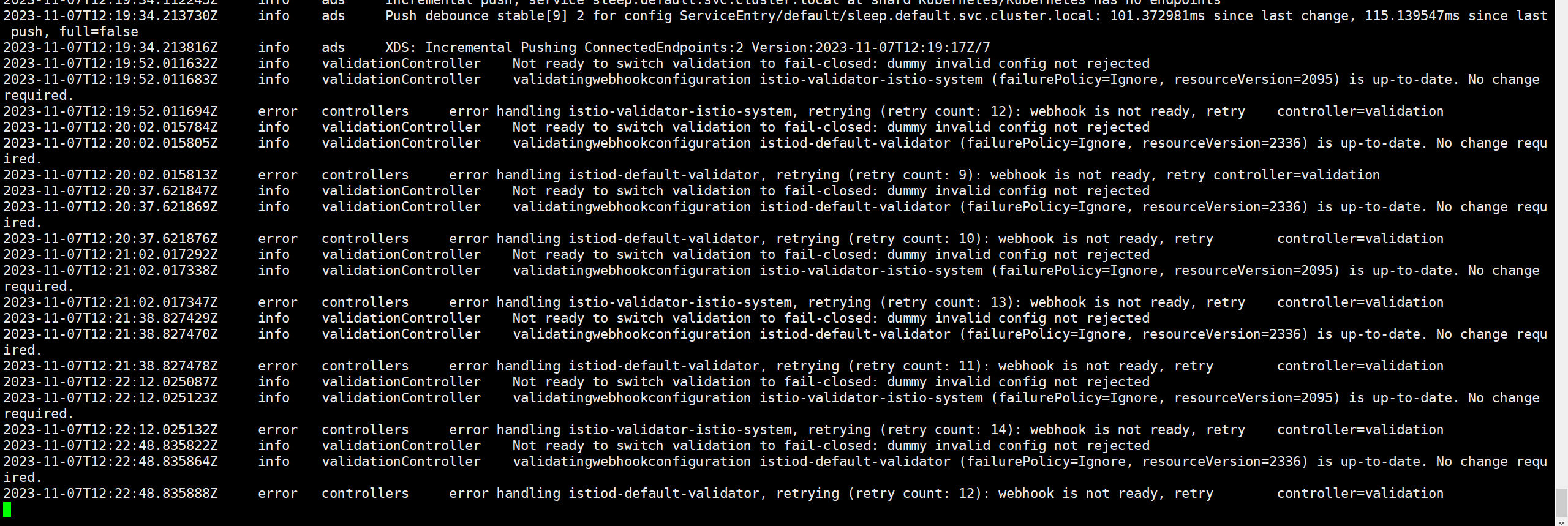
api-server日志:
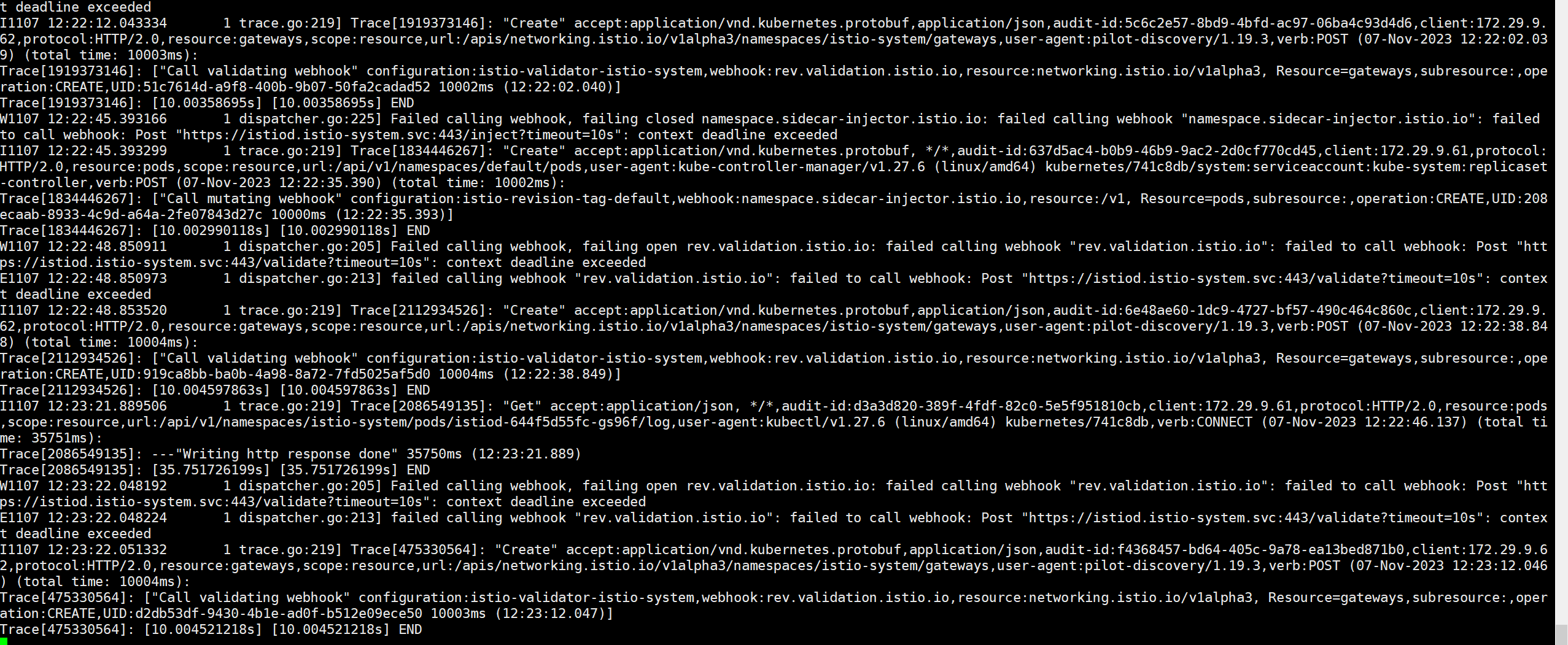
kubelet信息:

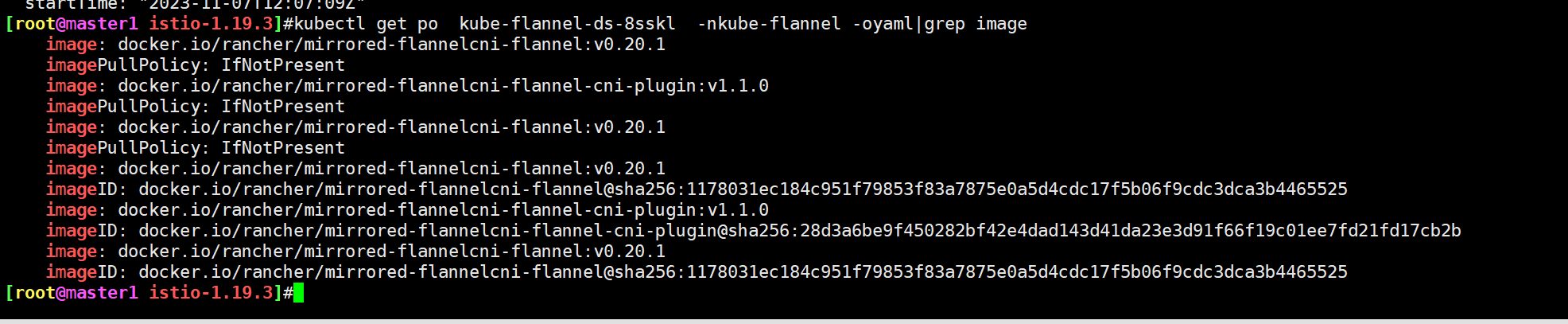
再次测试:2023年11月8日,升级cni flanel版本
- 自己当前flannel版本

- 老师测试成功的flannel版本:docker.io/flannel/flannel:v0.22.2
- 这里到flannel github下载v0.22.2版本,进行安装再测试
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flannel-io/flannel/v0.20.1/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/flannel-io/flannel/v0.20.1/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
https://github.com/flannel-io/flannel/releases/download/v0.22.2/kube-flannel.yml
https://ghps.cc/https://github.com/flannel-io/flannel/releases/download/v0.22.2/kube-flannel.yml
wget https://ghps.cc/https://github.com/flannel-io/flannel/releases/download/v0.22.2/kube-flannel.yml先卸载原来版本的kube-falnnel:
[root@master1 ~]#kubectl delete -f kube-flannel.yml
namespace "kube-flannel" deleted
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "flannel" deleted
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io "flannel" deleted
serviceaccount "flannel" deleted
configmap "kube-flannel-cfg" deleted
daemonset.apps "kube-flannel-ds" deleted下载好后直接安装:
[root@master1 install-flannel]#kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml
namespace/kube-flannel created
serviceaccount/flannel created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/flannel created
configmap/kube-flannel-cfg created
daemonset.apps/kube-flannel-ds created
[root@master1 install-flannel]#- 查看安装好的新版本flannel
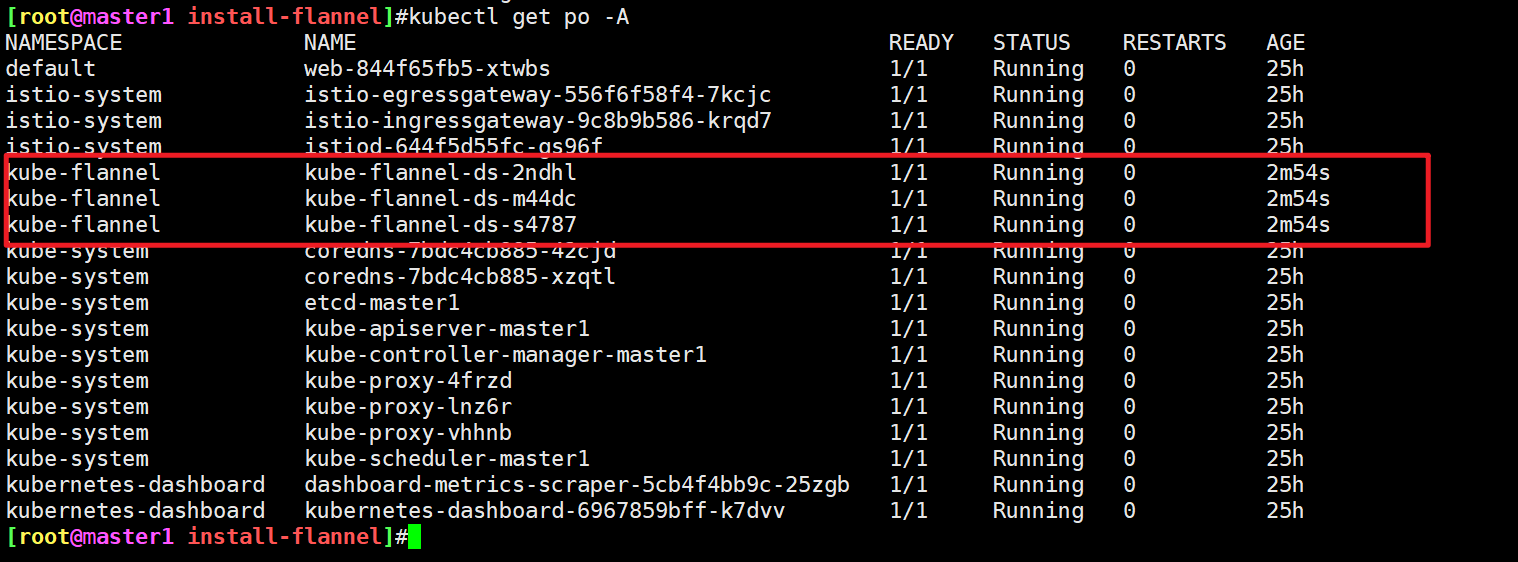

[root@master1 install-flannel]#kubectl get ds kube-flannel-ds -nkube-flannel -oyaml|grep image
image: docker.io/flannel/flannel:v0.22.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
image: docker.io/flannel/flannel-cni-plugin:v1.2.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
image: docker.io/flannel/flannel:v0.22.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent终于可以了:==。。。==
- 再次部署istio sidecar测试
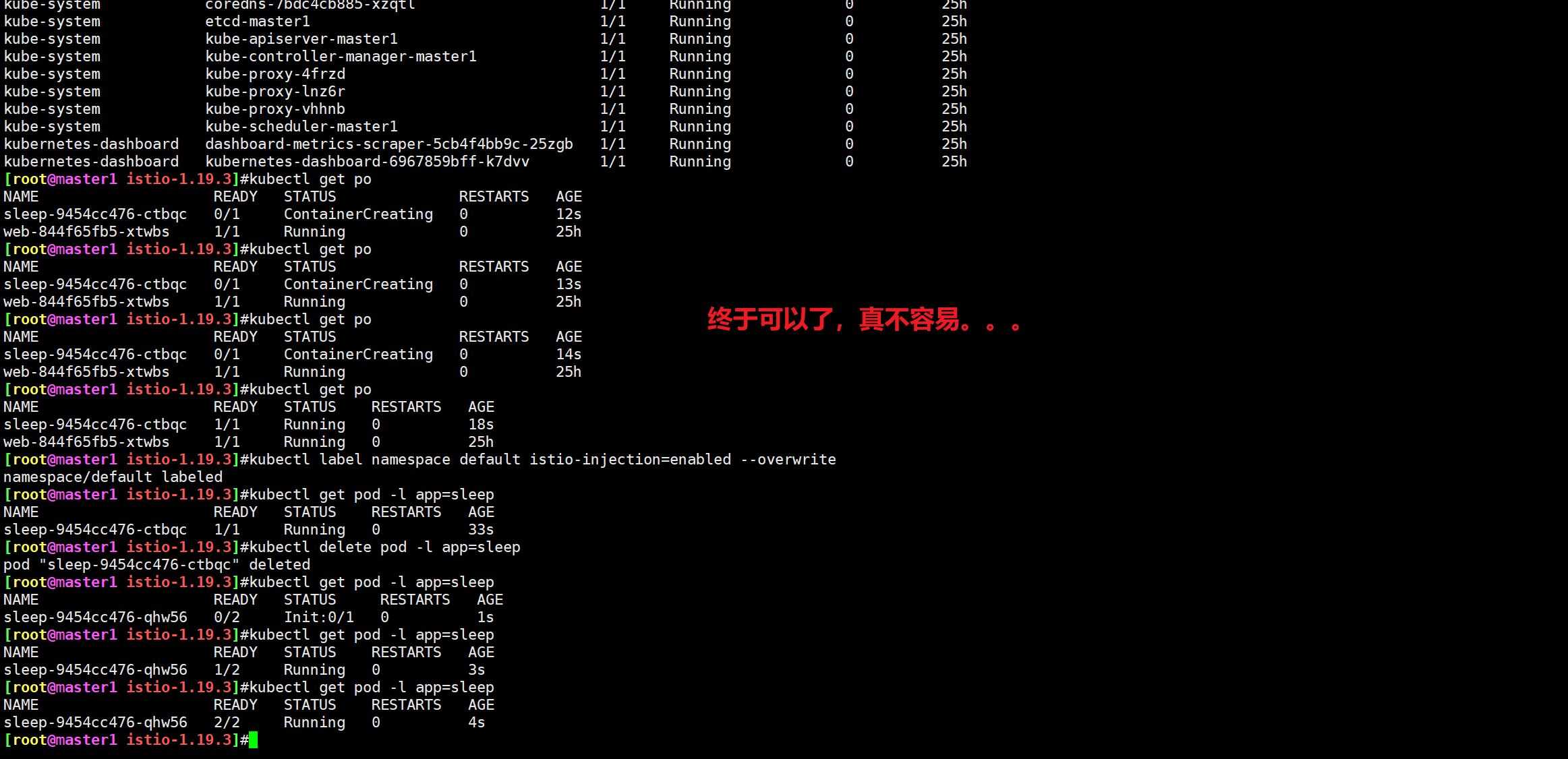
结束。😘
3、BookInfo 示例应用
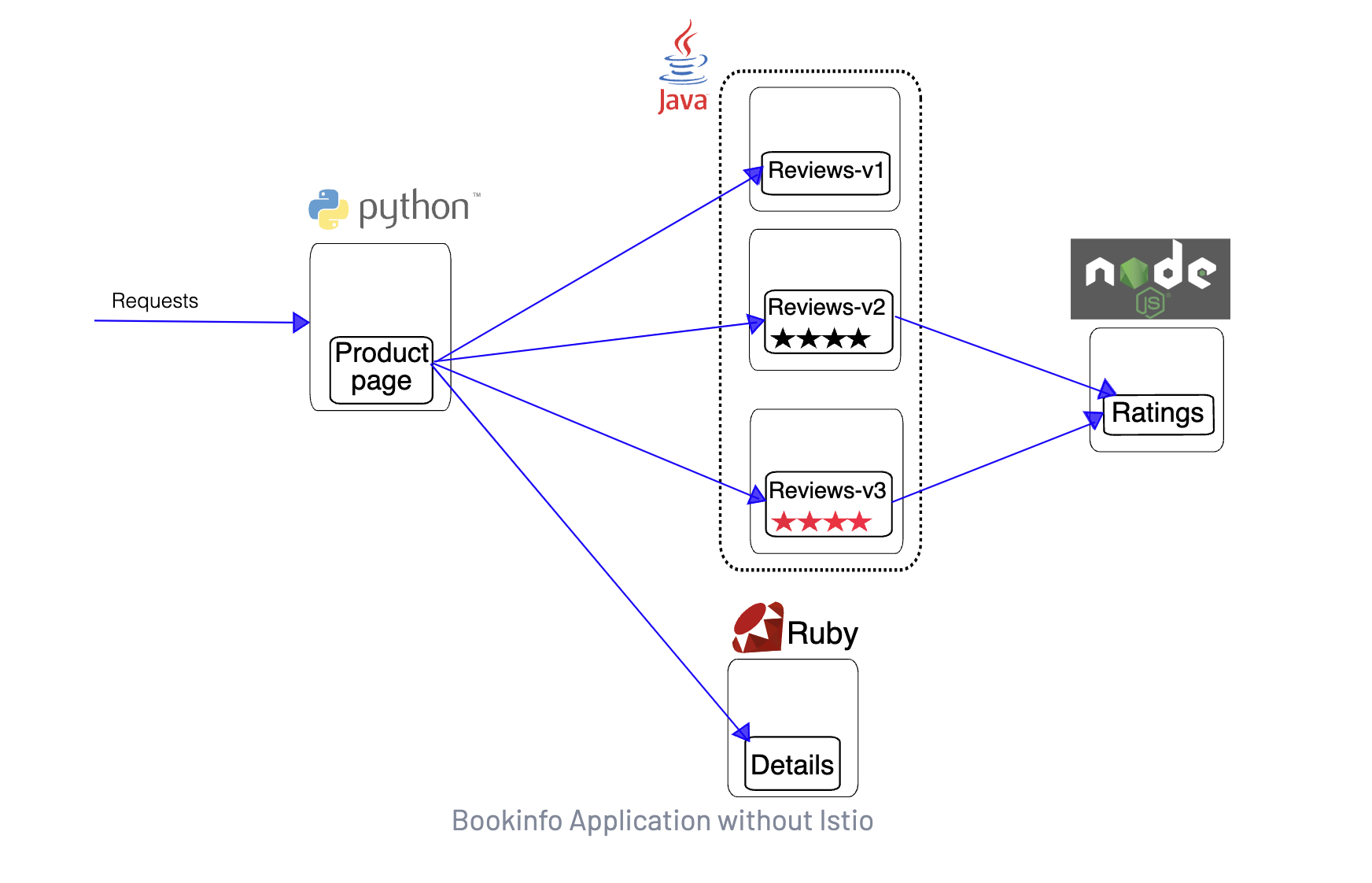
Bookinfo 是一个非常经典的微服务示例项目,它由四个独立的微服务组成,每个微服务都是用不同的语言编写的,可以用于演示多种 Istio 特性的应用。这个应用模仿在线书店的一个分类,显示一本书的信息,页面上会显示一本书的描述,书籍的细节(ISBN、页数等),以及关于这本书的一些评论。
Bookinfo 应用分为以下四个单独的微服务:
productpage:这个微服务会调用details和reviews两个微服务,用来生成页面。details:这个微服务中包含了书籍的信息。reviews:这个微服务中包含了书籍相关的评论,它还会调用ratings微服务。ratings:这个微服务中包含了由书籍评价组成的评级信息。
reviews 微服务有 3 个版本:
v1版本不会调用ratings服务。v2版本会调用ratings服务,并使用 1 到 5 个黑色星形图标来显示评分信息。v3版本会调用ratings服务,并使用 1 到 5 个红色星形图标来显示评分信息。
下图展示了这个应用的端到端架构。
现在我们来为 Bookinfo 应用提供 Istio 支持,无需对应用自身做出任何改变。只要简单的在 Istio 环境中对服务进行配置和运行即可,其实就是把 Envoy Sidecar 注入到每个服务之中。最终的部署结果将如下图所示:
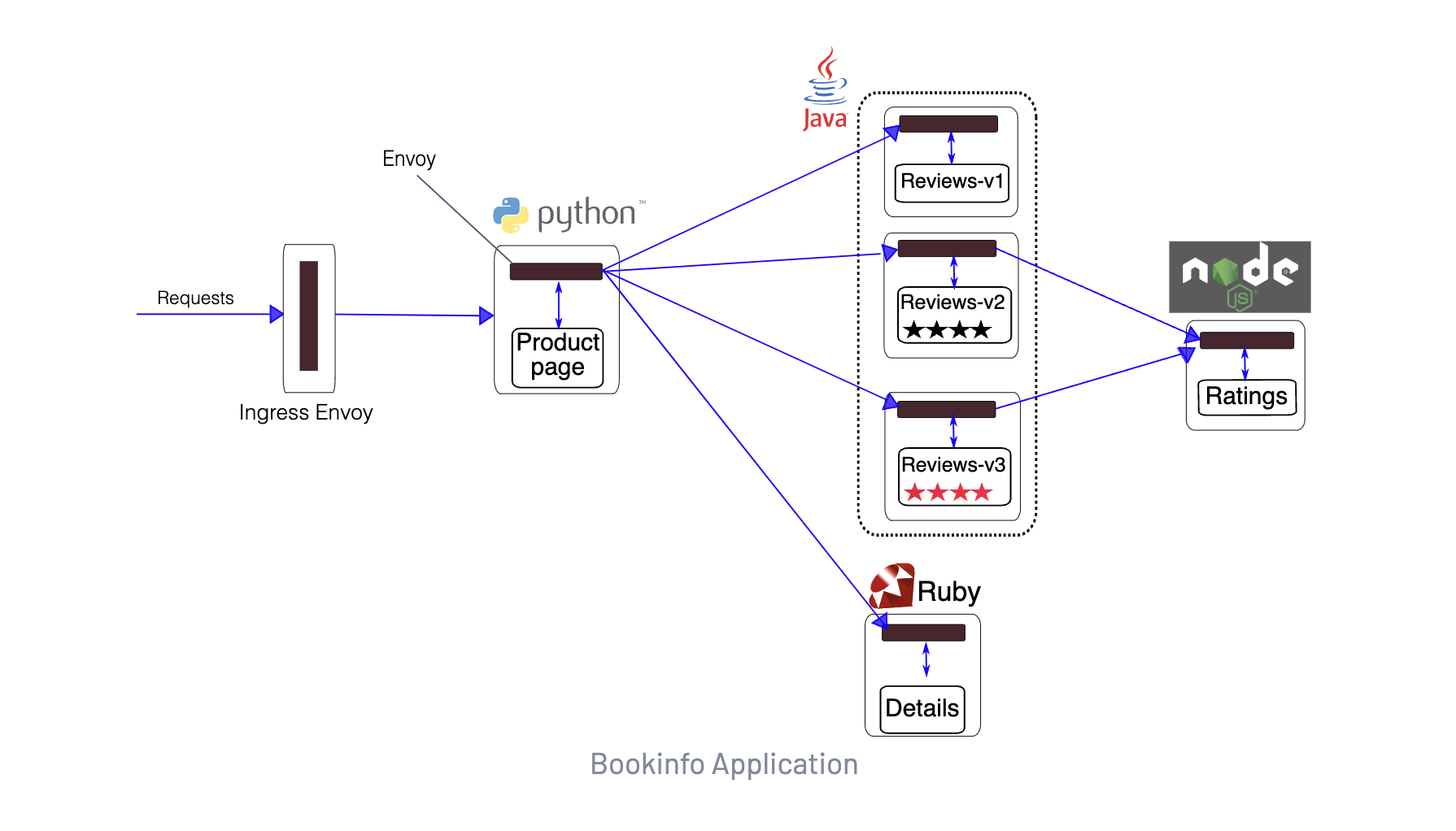
所有的微服务都和 Envoy Sidecar 集成在一起,服务所有的出入流量都被 Sidecar 所劫持,然后我们就可以利用 Istio 控制平面为应用提供服务路由、遥测数据收集以及策略实施等服务治理功能了。
==🚩 实战:BookInfo 示例应用-2023.11.5(测试成功)==
实验环境:
k8s v1.25.4(containerd://1.6.10)
[root@master1 ~]#istioctl version
client version: 1.19.3
control plane version: 1.19.3
data plane version: 1.19.3 (8 proxies)实验软件:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1pMnJxgL63oTlGFlhrfnXsA?pwd=7yqb 提取码:7yqb 2023.11.5-实战:BookInfo 示例应用-2023.11.5(测试成功)

实验步骤:
graph LR
A[实战步骤] -->B(1️⃣ 部署示例应用)
A[实战步骤] -->C(2️⃣ 对外暴露应用)
A[实战步骤] -->D(3️⃣ 查看 Dashboard)==1.部署示例应用==
🍀
我们首先进入 Istio 安装目录,该目录中的 samples 目录中就包含了 Bookinfo 部署到 Kubernetes 集群中的配置文件,我们只需要为这些资源注入 Sidecar。这里我们为 default 命名空间打上标签 istio-injection=enabled,开启自动注入功能即可:
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled --overwrite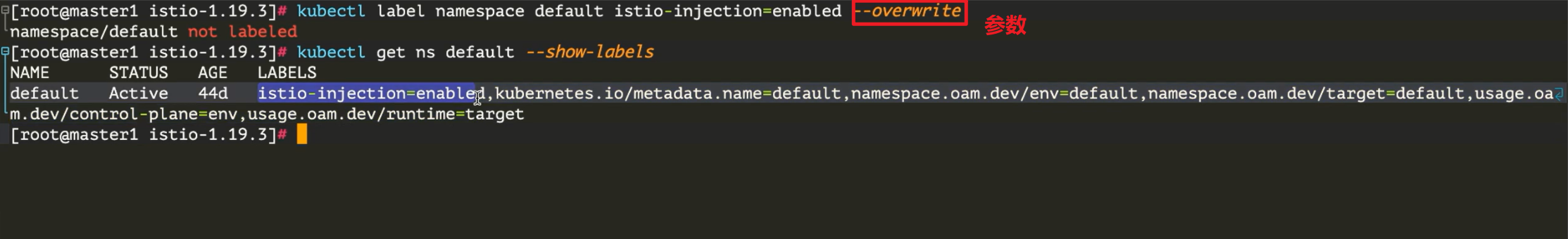
🍀
然后只需要使用 kubectl 正常部署应用即可:
$ kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
service/details created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-details created
deployment.apps/details-v1 created
service/ratings created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-ratings created
deployment.apps/ratings-v1 created
service/reviews created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-reviews created
deployment.apps/reviews-v1 created
deployment.apps/reviews-v2 created
deployment.apps/reviews-v3 created
service/productpage created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-productpage created
deployment.apps/productpage-v1 created注意:
如果在安装过程中禁用了 Sidecar 自动注入功能而选择手动注入 Sidecar,可以使用 istioctl kube-inject 命令来手动注入:
$ kubectl apply -f <(istioctl kube-inject -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml)自己本次手动注入:(我的自动注入有点问题,这里使用手动注入方式)
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl apply -f <(istioctl kube-inject -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml)
service/details created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-details created
deployment.apps/details-v1 created
service/ratings created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-ratings created
deployment.apps/ratings-v1 created
service/reviews created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-reviews created
deployment.apps/reviews-v1 created
deployment.apps/reviews-v2 created
deployment.apps/reviews-v3 created
service/productpage created
serviceaccount/bookinfo-productpage created
deployment.apps/productpage-v1 created🍀
上面的命令会启动全部的四个服务,其中也包括了 reviews 服务的三个版本(v1、v2 以及 v3)。
隔一会儿,我们可以查看下 Pod 的状态:
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
details-v1-5f4d584748-97stc 2/2 Running 0 12m
productpage-v1-564d4686f-z7fwn 2/2 Running 0 12m
ratings-v1-686ccfb5d8-cvlcq 2/2 Running 0 12m
reviews-v1-86896b7648-rrjxv 2/2 Running 0 12m
reviews-v2-b7dcd98fb-kk8fv 2/2 Running 0 12m
reviews-v3-5c5cc7b6d-c4wf5 2/2 Running 0 12m
$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
details ClusterIP 10.98.49.69 <none> 9080/TCP 13m
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 44d
productpage ClusterIP 10.101.255.202 <none> 9080/TCP 13m
ratings ClusterIP 10.101.210.142 <none> 9080/TCP 13m
reviews ClusterIP 10.106.93.80 <none> 9080/TCP 13m[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get po
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
details-v1-76bdcd6b59-9p5gh 2/2 Running 0 18m
productpage-v1-d594c998-x8s6k 2/2 Running 0 18m
ratings-v1-64694b479f-qcbcm 2/2 Running 0 18m
reviews-v1-68f98444cd-szhrv 2/2 Running 0 18m
reviews-v2-6c9b87bd47-t4l9c 2/2 Running 0 18m
reviews-v3-9569b895b-jr29m 2/2 Running 0 18m
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
details ClusterIP 10.107.100.41 <none> 9080/TCP 19m
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 7d17h
productpage ClusterIP 10.110.115.123 <none> 9080/TCP 19m
ratings ClusterIP 10.101.72.27 <none> 9080/TCP 19m
reviews ClusterIP 10.111.206.146 <none> 9080/TCP 19m当每个 Pod 准备就绪时,Istio Sidecar 将伴随应用一起部署。
🍀
要确认 Bookinfo 应用是否正在运行,我们可以在某个 Pod 中用 curl 命令对应用发送请求来验证,例如 ratings:
$ kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -l app=ratings -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')" -c ratings -- curl -sS productpage:9080/productpage | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"
<title>Simple Bookstore App</title>如果能够正常数据,说明应用已经部署成功了,而且已经被 Istio 管控起来了。
==2.对外暴露应用==
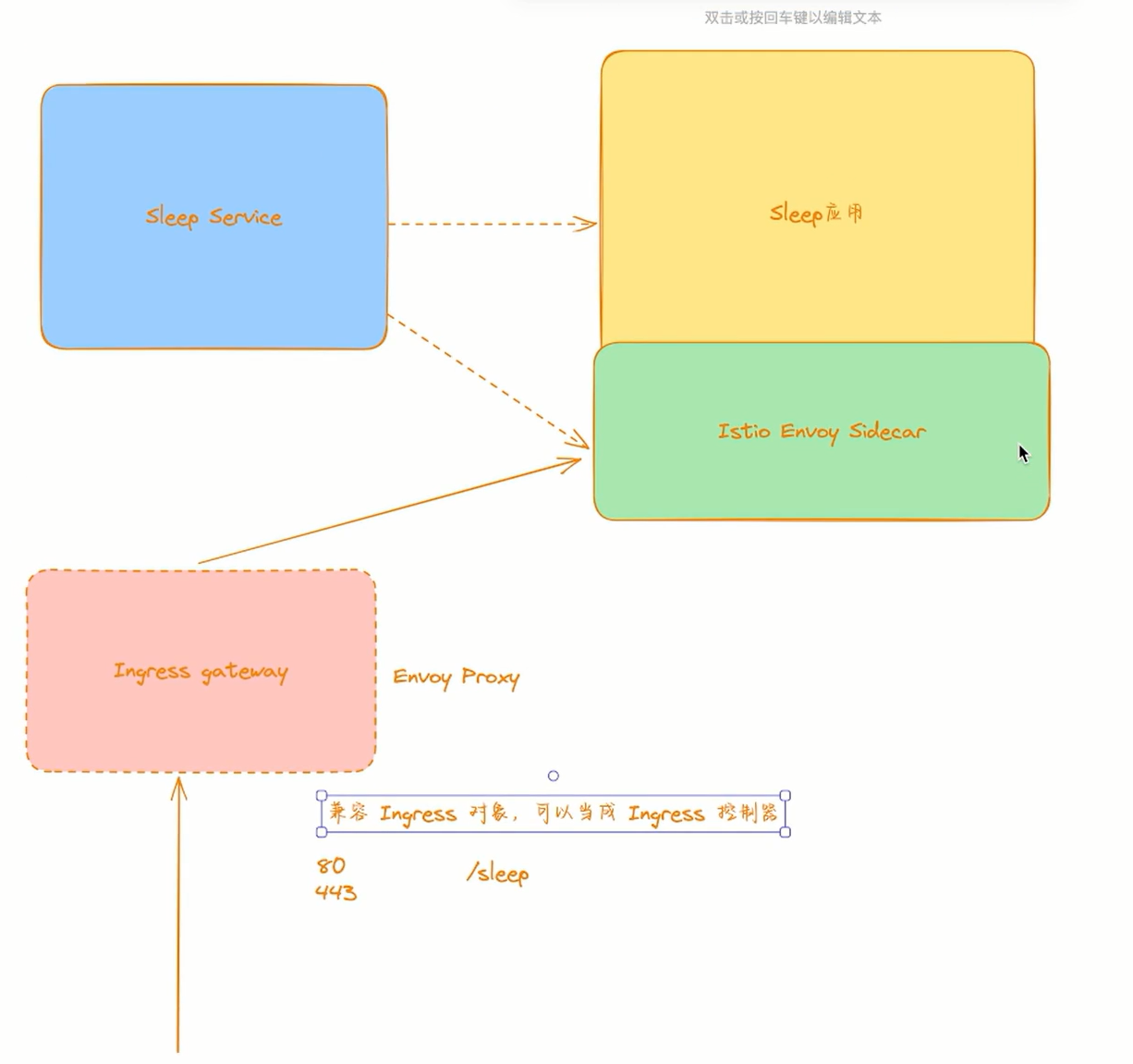
上面我们已经将 Bookinfo 应用部署成功了,但是还不能被外界访问,如果没有 Istio 的情况下我们可以直接通过 NodePort 或者 Ingress 的方式来对外进行暴露,但是现在我们使用了 Istio,需要创建 ==Istio 入站网关(Ingress Gateway)==来对外暴露应用了。
🍀
在 samples 目录下面有一个 Bookinfo 对外暴露的配置文件 bookinfo-gateway.yaml,这个配置文件中定义了一个 Gateway 和一个 VirtualService 对象,Gateway 定义了入站流量的端口和协议,VirtualService 定义了流量的路由规则,内容如下所示:
# samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gateway
spec:
selector: # 如果使用的是 Helm 方式安装,则默认应该是 istio=ingress 标签
istio: ingressgateway # 匹配 ingress gateway pod 的标签(kubectl get pods -l istio=ingressgateway -n istio-system)
servers:
- port:
number: 8080
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "*"
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: bookinfo
spec:
hosts:
- "*"
gateways:
- bookinfo-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
exact: /productpage
- uri:
prefix: /static
- uri:
exact: /login
- uri:
exact: /logout
- uri:
prefix: /api/v1/products
route:
- destination:
host: productpage
port:
number: 9080这两个资源对象我们后面还会详细讲解的,现在我们只需要知道这两个资源对象是用来定义入站流量的端口和协议以及流量的路由规则的即可。如果你联想到前面我们讲解的 Envoy 配置,那么你就会发现这两个资源对象其实分别对应着 Envoy 配置中的 Listener 和 VirtualHosts(包括 Cluster),只不过这里是用我们更熟悉的 Kubernetes CRD 的方式来进行配置的,当我们创建了这两个资源对象后,Istio 控制平面会自动把这些配置下发到 Envoy Sidecar 中,然后 Envoy Sidecar 就会根据这些配置来进行流量的路由了。
🍀
接下来我们执行下面的命令来把应用关联到 Istio 网关:
$ kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
gateway.networking.istio.io/bookinfo-gateway created
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/bookinfo created🍀
然后我们就可以通过 istio-ingressgateway 这个统一的入口来访问应用了,我们可以通过 kubectl get svc -n istio-system 命令来查看下 istio-ingressgateway 的地址:
$ kubectl get svc istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.103.227.57 <pending> 15021:32459/TCP,80:31896/TCP,443:30808/TCP,31400:31535/TCP,15443:30761/TCP 155m[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#kubectl get svc istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
istio-ingressgateway LoadBalancer 10.104.174.171 <pending> 15021:32479/TCP,80:31814/TCP,443:31263/TCP,31400:32543/TCP,15443:30806/TCP 13h由于我们这里没有负载均衡器,所以 EXTERNAL-IP 的值一直是 <pending> 状态,这种情况下我们可以用 NodePort 来访问网关。可以通过如下命令获取 HTTP 和 HTTPS 的访问端口:
export INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].nodePort}')
export SECURE_INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n istio-system get service istio-ingressgateway -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="https")].nodePort}')然后获取集群中任意一个节点的 IP 地址:
export INGRESS_HOST=$(kubectl get po -l istio=ingressgateway -n istio-system -o jsonpath='{.items[0].status.hostIP}')设置环境变量 GATEWAY_URL:
export GATEWAY_URL=$INGRESS_HOST:$INGRESS_PORT确保 IP 地址和端口均成功地赋值给了环境变量:
$ echo "$GATEWAY_URL"
192.168.0.20:31896
[root@master1 istio-1.19.3]#echo "$GATEWAY_URL"
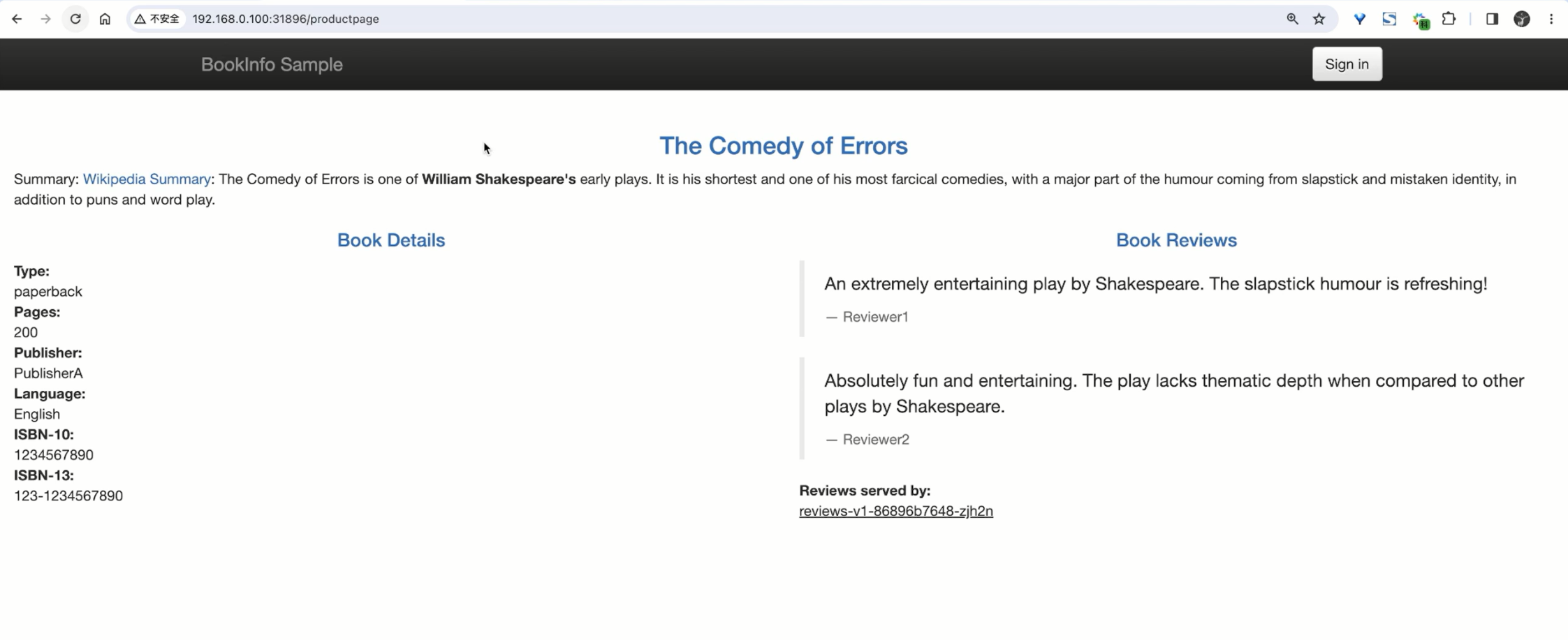
172.29.9.62:31814这样我们就得到了 Istio 入口网关的访问地址,然后我们只需要在浏览器中通过 http://$GATEWAY_URL/productpage 即可访问到 Bookinfo 应用了。

注意:



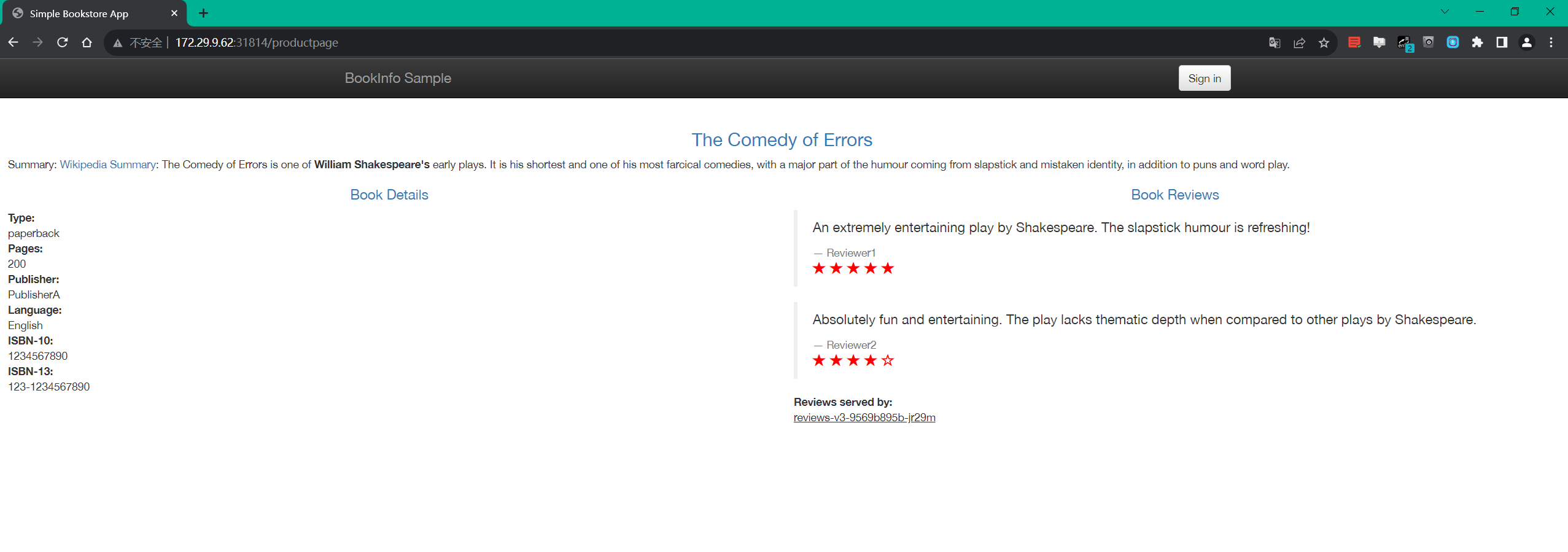
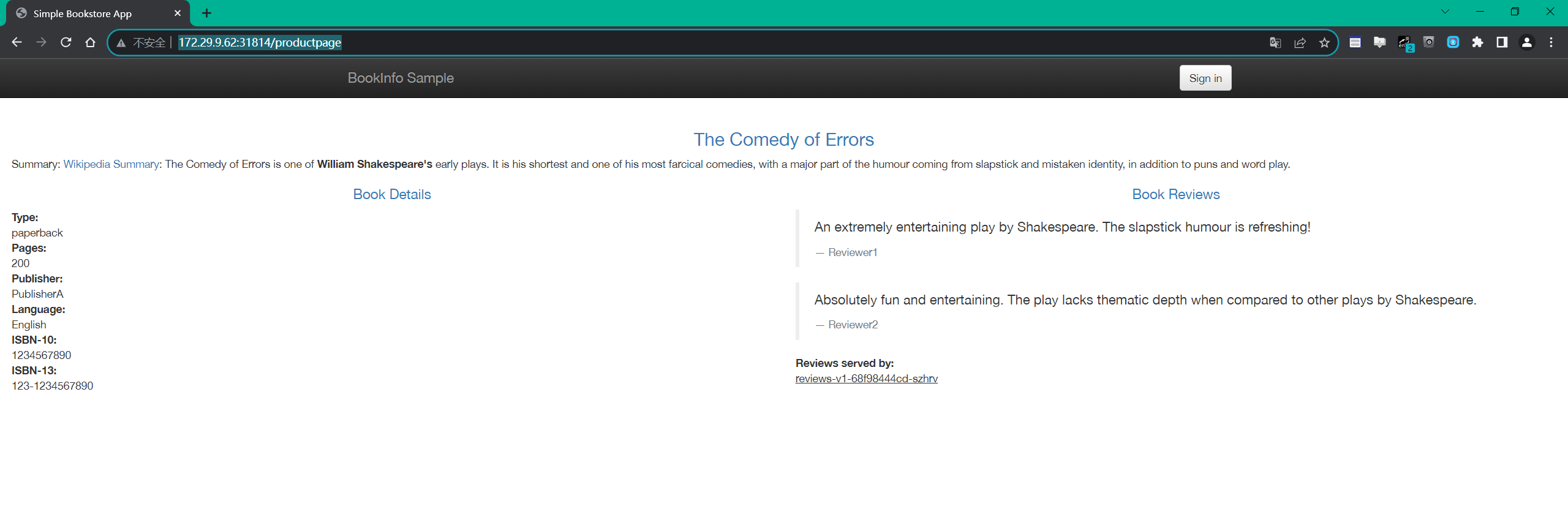
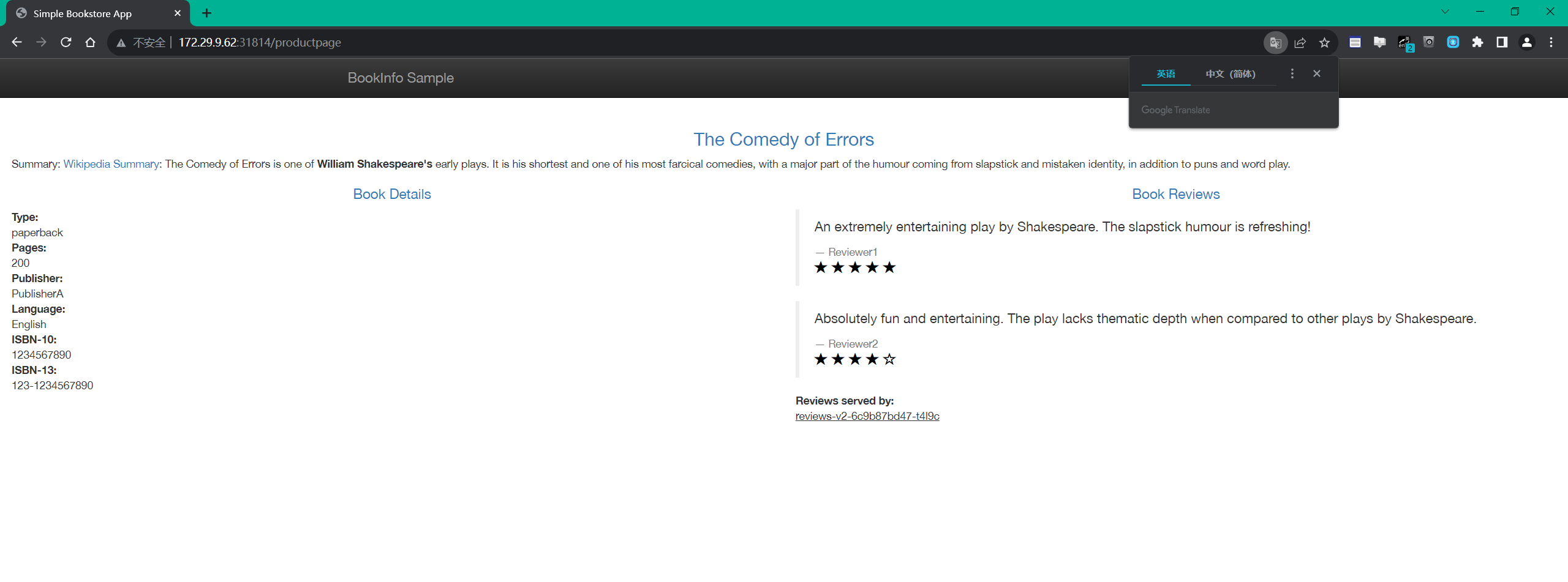
==3.查看 Dashboard==
Istio 和几个遥测应用做了集成。遥测能帮我们了解服务网格的结构、展示网络的拓扑结构、分析网格的健康状态。
🍀
我们可以使用下面的方式来安装 Kiali,包括 Prometheus、Grafana 以及 jaeger。
$ kubectl apply -f samples/addons
$ kubectl rollout status deployment/kiali -n istio-system
Waiting for deployment "kiali" rollout to finish: 0 of 1 updated replicas are available...
deployment "kiali" successfully rolled out
$ kubectl get pods -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
grafana-5f9b8c6c5d-jv65v 1/1 Running 0 6m23s
istio-egressgateway-556f6f58f4-hkzdd 1/1 Running 0 177m
istio-ingressgateway-9c8b9b586-s6s48 1/1 Running 0 177m
istiod-644f5d55fc-zz2zh 1/1 Running 0 179m
jaeger-db6bdfcb4-qpmmv 1/1 Running 0 6m23s
kiali-7c9d5f9f96-cp4mb 1/1 Running 0 6m23s
prometheus-5d5d6d6fc-2gtxm 2/2 Running 0 6m22s如果在安装插件时出错,再运行一次命令。有一些和时间相关的问题,再次运行就能解决。
🍀
安装完成后我们可以使用 istioctl dashboard 命令来开启访问 Kiali 面板。
$ istioctl dashboard kiali --address 0.0.0.0
http://0.0.0.0:20001/kiali
# http://172.29.9.61:20001/kiali/
🍀
在左侧的导航菜单,选择 Graph ,然后在 Namespace 下拉列表中,选择 default。

丢失图片
🍀
要查看链路追踪数据,必须向服务发送请求。请求的数量取决于 Istio 的采样率,采样率在安装 Istio 时设置,默认采样速率为 1%。也就是说在第一个 tracing 可见之前,需要发送至少 100 个请求:
$ for i in $(seq 1 100); do curl -s -o /dev/null "http://$GATEWAY_URL/productpage"; done

丢失图片
🍀
Kiali 的仪表板展示了网格的概览以及 Bookinfo 示例应用的各个服务之间的关系。 它还提供过滤器来可视化流量的流动。
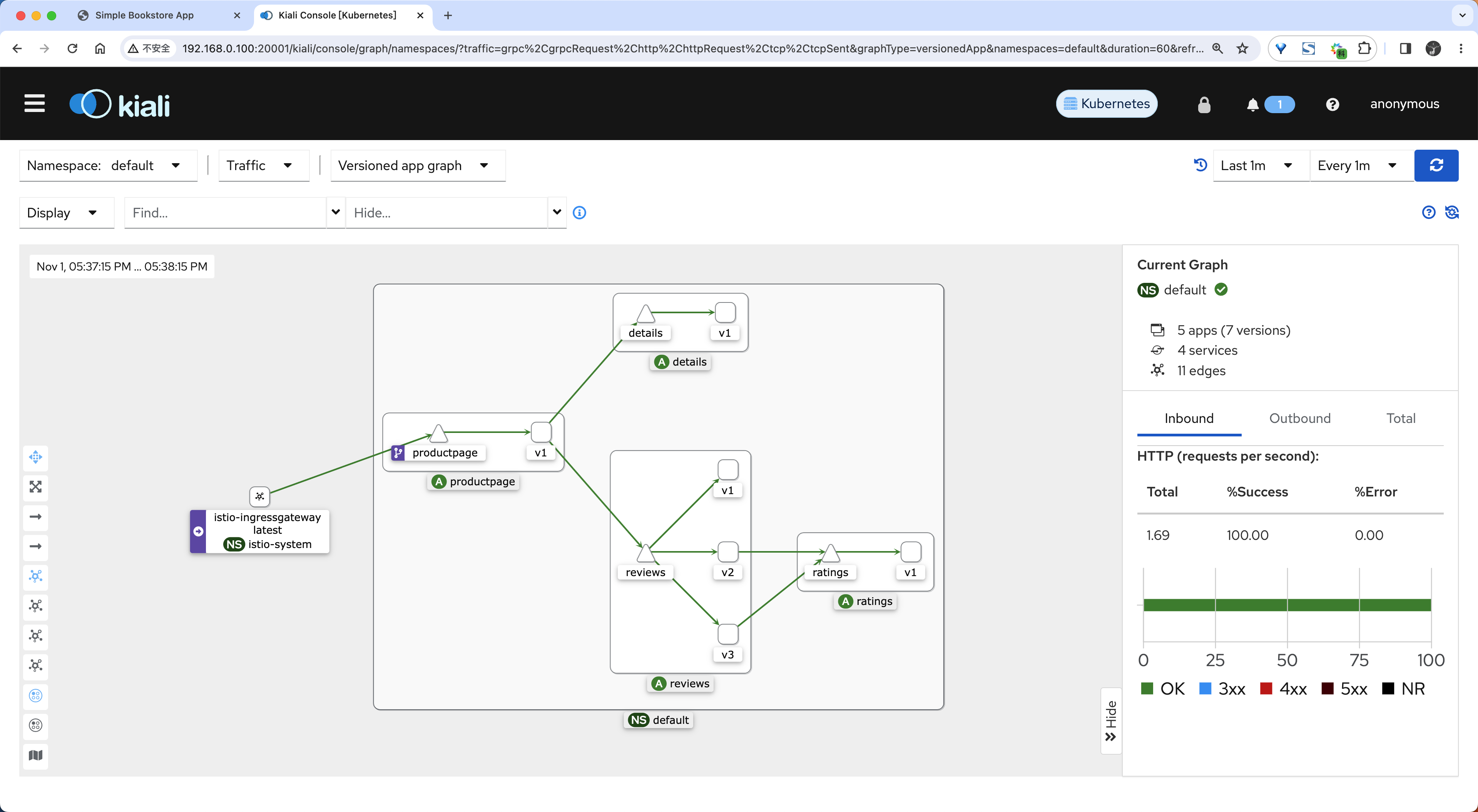
丢失图片
到这里我们就完成了 Bookinfo 示例应用的部署,以及对外暴露应用的配置,接下来我们就可以开始学习 Istio 的核心功能了。
⚠️ 注意:这里的pod要依赖pvc
本次这里就暂不安装nfs了,记录下即可。
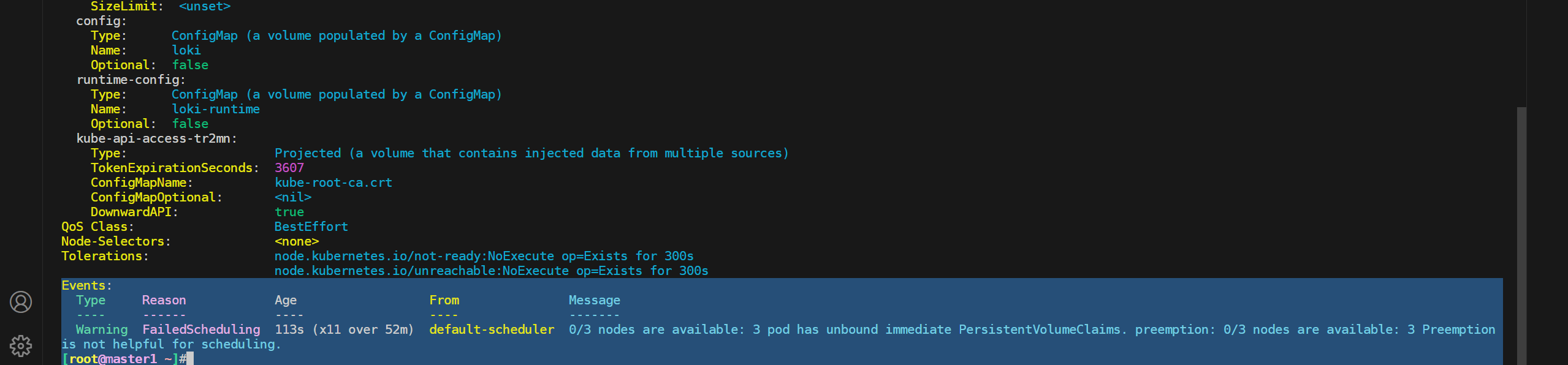
4、istioctl如何卸载istiod
🍀
官方删除istiod
卸载 Istio
要从集群中完整卸载 Istio,运行下面命令:
$ istioctl uninstall --purge可选的 --purge 参数将移除所有 Istio 资源,包括可能被其他 Istio 控制平面共享的、集群范围的资源。
或者,只移除指定的 Istio 控制平面,运行以下命令:
$ istioctl uninstall <your original installation options>或
$ istioctl manifest generate <your original installation options> | kubectl delete --ignore-not-found=true -f -控制平面的命名空间(例如:istio-system)默认不会被移除。 如果确认不再需要,用下面命令移除该命名空间:
$ kubectl delete namespace istio-system🍀
gpt回答:
istioctl如何卸载istiod ?
要卸载 Istio 中的 istiod,您可以使用 Istio 的命令行工具 istioctl 来执行卸载操作。请注意,卸载 istiod 会从集群中删除 Istio 控制平面的组件。
以下是卸载 istiod 的基本步骤:
- 打开终端并使用
istioctl连接到您的 Kubernetes 集群。确保已经安装 Istio 并配置好istioctl。 - 运行以下命令卸载
istiod:
istioctl uninstall istiod这将删除 istiod 及其关联的组件,例如 Pilot、Galley 和 Mixer。
- 确认卸载操作完成。这可能需要一些时间,具体时间取决于您的集群规模和网络状况。
请注意,卸载 istiod 后,您的 Istio 控制平面将不再运行,这可能会影响已部署的应用程序。如果需要重新安装 Istio 或者只是想卸载 Istio 控制平面而保留 sidecar 代理(Envoy)在应用程序中,可以根据需要重新安装 Istio 控制平面的特定组件。
在执行任何卸载操作之前,请务必备份您的配置和数据,以免丢失重要信息。根据您的需求和集群配置,还可能需要对卸载过程进行适当的自定义。
🍀
自己测试过程:
[root@master1 ~]#istioctl uninstall --purge
All Istio resources will be pruned from the cluster
Proceed? (y/N) Y
Removed IstioOperator:istio-system:installed-state.
Removed Deployment:istio-system:istio-egressgateway.
Removed Deployment:istio-system:istio-ingressgateway.
Removed Deployment:istio-system:istiod.
Removed Service:istio-system:istio-egressgateway.
Removed Service:istio-system:istio-ingressgateway.
Removed Service:istio-system:istiod.
Removed ConfigMap:istio-system:istio.
Removed ConfigMap:istio-system:istio-sidecar-injector.
Removed Pod:istio-system:istio-egressgateway-8477dd44c4-9q8d4.
Removed Pod:istio-system:istio-ingressgateway-5c58fcb646-jk4fh.
Removed Pod:istio-system:istiod-5d9595449c-b2pmc.
Removed ServiceAccount:istio-system:istio-egressgateway-service-account.
Removed ServiceAccount:istio-system:istio-ingressgateway-service-account.
Removed ServiceAccount:istio-system:istio-reader-service-account.
Removed ServiceAccount:istio-system:istiod.
Removed RoleBinding:istio-system:istio-egressgateway-sds.
Removed RoleBinding:istio-system:istio-ingressgateway-sds.
Removed RoleBinding:istio-system:istiod.
Removed Role:istio-system:istio-egressgateway-sds.
Removed Role:istio-system:istio-ingressgateway-sds.
Removed Role:istio-system:istiod.
Removed PodDisruptionBudget:istio-system:istio-egressgateway.
Removed PodDisruptionBudget:istio-system:istio-ingressgateway.
Removed PodDisruptionBudget:istio-system:istiod.
Removed MutatingWebhookConfiguration::istio-revision-tag-default.
Removed MutatingWebhookConfiguration::istio-sidecar-injector.
Removed ValidatingWebhookConfiguration::istio-validator-istio-system.
Removed ValidatingWebhookConfiguration::istiod-default-validator.
Removed ClusterRole::istio-reader-clusterrole-istio-system.
Removed ClusterRole::istiod-clusterrole-istio-system.
Removed ClusterRole::istiod-gateway-controller-istio-system.
Removed ClusterRoleBinding::istio-reader-clusterrole-istio-system.
Removed ClusterRoleBinding::istiod-clusterrole-istio-system.
Removed ClusterRoleBinding::istiod-gateway-controller-istio-system.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::authorizationpolicies.security.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::destinationrules.networking.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::envoyfilters.networking.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::gateways.networking.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::istiooperators.install.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::peerauthentications.security.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::proxyconfigs.networking.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::requestauthentications.security.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::serviceentries.networking.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::sidecars.networking.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::telemetries.telemetry.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::virtualservices.networking.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::wasmplugins.extensions.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::workloadentries.networking.istio.io.
Removed CustomResourceDefinition::workloadgroups.networking.istio.io.
? Uninstall complete [root@master1 ~]#
[root@master1 ~]#kubectl get po -A
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-flannel kube-flannel-ds-pjfww 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-flannel kube-flannel-ds-pzt57 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-flannel kube-flannel-ds-slqjx 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-system coredns-7b884d5cb7-nvg5b 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-system coredns-7b884d5cb7-zg9x6 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-system etcd-master1 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-system kube-apiserver-master1 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-system kube-controller-manager-master1 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-system kube-proxy-dqzq4 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-system kube-proxy-jf46d 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-system kube-proxy-xvmdd 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kube-system kube-scheduler-master1 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kubernetes-dashboard dashboard-metrics-scraper-64bcc67c9c-tm42j 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard-5c8bd6b59-stxgx 1/1 Running 1 (22h ago) 7d4h
[root@master1 ~]#可以看到istio相关的3个pod资源被清除掉了。
清除istio-system
[root@master1 ~]#kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 7d4h
istio-system Active 31h
kube-flannel Active 7d4h
kube-node-lease Active 7d4h
kube-public Active 7d4h
kube-system Active 7d4h
kubernetes-dashboard Active 7d4h
[root@master1 ~]#kubectl delete ns istio-system
namespace "istio-system" deleted
[root@master1 ~]#kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 7d4h
kube-flannel Active 7d4h
kube-node-lease Active 7d4h
kube-public Active 7d4h
kube-system Active 7d4h
kubernetes-dashboard Active 7d4h
[root@master1 ~]#1
